Systematic analysis of RNA-binding proteins identifies targetable therapeutic vulnerabilities in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 38561347
- PMCID: PMC10984982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47031-y
Systematic analysis of RNA-binding proteins identifies targetable therapeutic vulnerabilities in osteosarcoma
Abstract
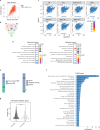
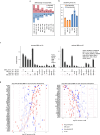
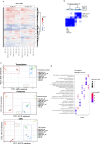
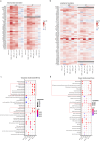
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor with a strong tendency to metastasize, limiting the prognosis of affected patients. Genomic, epigenomic and transcriptomic analyses have demonstrated the exquisite molecular complexity of this tumor, but have not sufficiently defined the underlying mechanisms or identified promising therapeutic targets. To systematically explore RNA-protein interactions relevant to OS, we define the RNA interactomes together with the full proteome and the transcriptome of cells from five malignant bone tumors (four osteosarcomata and one malignant giant cell tumor of the bone) and from normal mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts. These analyses uncover both systematic changes of the RNA-binding activities of defined RNA-binding proteins common to all osteosarcomata and individual alterations that are observed in only a subset of tumors. Functional analyses reveal a particular vulnerability of these tumors to translation inhibition and a positive feedback loop involving the RBP IGF2BP3 and the transcription factor Myc which affects cellular translation and OS cell viability. Our results thus provide insight into potentially clinically relevant RNA-binding protein-dependent mechanisms of osteosarcoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

