CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer
- PMID: 38561369
- PMCID: PMC10985117
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46735-5
CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer
Abstract
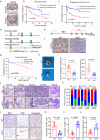
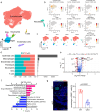
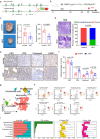
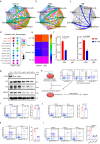
Interplay between innate and adaptive immune cells is important for the antitumor immune response. However, the tumor microenvironment may turn immune suppressive, and tumor associated macrophages are playing a role in this transition. Here, we show that CD276, expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), play a role in diminishing the immune response against tumors. Using a model of tumors induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine in BLCA male mice we show that genetic ablation of CD276 in TAMs blocks efferocytosis and enhances the expression of the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) of TAMs. This in turn increases CD4 + and cytotoxic CD8 + T cell infiltration of the tumor. Combined single cell RNA sequencing and functional experiments reveal that CD276 activates the lysosomal signaling pathway and the transcription factor JUN to regulate the expression of AXL and MerTK, resulting in enhanced efferocytosis in TAMs. Proving the principle, we show that simultaneous blockade of CD276 and PD-1 restrain tumor growth better than any of the components as a single intervention. Taken together, our study supports a role for CD276 in efferocytosis by TAMs, which is potentially targetable for combination immune therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

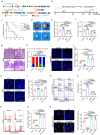
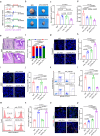
References
-
- Patel VG, Oh WK, Galsky MD. Treatment of muscle-invasive and advanced bladder cancer in 2020. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70:404–423. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82173362/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81872409/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82273414/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81974443/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

