Diversity analysis of sea anemone peptide toxins in different tissues of Heteractis crispa based on transcriptomics
- PMID: 38561372
- PMCID: PMC10985097
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58402-2
Diversity analysis of sea anemone peptide toxins in different tissues of Heteractis crispa based on transcriptomics
Abstract
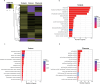
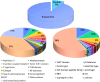
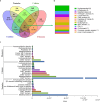
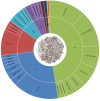
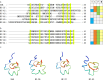
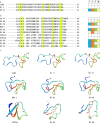
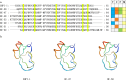
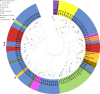
Peptide toxins found in sea anemones venom have diverse properties that make them important research subjects in the fields of pharmacology, neuroscience and biotechnology. This study used high-throughput sequencing technology to systematically analyze the venom components of the tentacles, column, and mesenterial filaments of sea anemone Heteractis crispa, revealing the diversity and complexity of sea anemone toxins in different tissues. A total of 1049 transcripts were identified and categorized into 60 families, of which 91.0% were proteins and 9.0% were peptides. Of those 1049 transcripts, 416, 291, and 307 putative proteins and peptide precursors were identified from tentacles, column, and mesenterial filaments respectively, while 428 were identified when the datasets were combined. Of these putative toxin sequences, 42 were detected in all three tissues, including 33 proteins and 9 peptides, with the majority of peptides being ShKT domain, β-defensin, and Kunitz-type. In addition, this study applied bioinformatics approaches to predict the family classification, 3D structures, and functional annotation of these representative peptides, as well as the evolutionary relationships between peptides, laying the foundation for the next step of peptide pharmacological activity research.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Venomics Reveals the Venom Complexity of Sea Anemone Heteractis magnifica.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jan 28;22(2):71. doi: 10.3390/md22020071. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38393042 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting venom of the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni: Omics techniques reveal the complete toxin arsenal of a well-studied sea anemone genus.J Proteomics. 2017 Aug 23;166:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Jul 21. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28739511
-
Kunitz-Type Peptide HCRG21 from the Sea Anemone Heteractis crispa Is a Full Antagonist of the TRPV1 Receptor.Mar Drugs. 2016 Dec 15;14(12):229. doi: 10.3390/md14120229. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27983679 Free PMC article.
-
Never, Ever Make an Enemy… Out of an Anemone: Transcriptomic Comparison of Clownfish Hosting Sea Anemone Venoms.Mar Drugs. 2022 Nov 23;20(12):730. doi: 10.3390/md20120730. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sea Anemones: Quiet Achievers in the Field of Peptide Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jan 8;10(1):36. doi: 10.3390/toxins10010036. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29316700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and cDNA cloning of four peptide toxins from the sea anemone Heteractis aurora.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024 Oct 28;30:e20240019. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2024-0019. eCollection 2024. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39530114 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale AI-Based Structure and Activity Prediction Analysis of ShK Domain Peptides from Sea Anemones in the South China Sea.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 16;23(2):85. doi: 10.3390/md23020085. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997209 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics.Mar Drugs. 2024 Oct 12;22(10):470. doi: 10.3390/md22100470. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452877 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated K+ Channel Modulation by Marine Toxins: Pharmacological Innovations and Therapeutic Opportunities.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 29;22(8):350. doi: 10.3390/md22080350. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics-driven exploration of genetic variation and peptide discovery in the sea anemones Anthopleura midori and Actinia equina.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 8;15(1):12061. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96976-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40200035 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HYYS2021A24/Hainan Medical University graduate innovation and entrepreneurship training program
- 22A200358/Hainan Province Health Industry Research Project
- 82060686/Chinese National Natural Science Foundation
- YSPTZX202132/Special scientific research project of Hainan academician innovation platform
- ZDYF2022SHFZ309/Hainan Provincial Key Point Research and Invention Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

