Differential cytokine expression in gastric tissues highlights helicobacter pylori's role in gastritis
- PMID: 38561502
- PMCID: PMC10984929
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58407-x
Differential cytokine expression in gastric tissues highlights helicobacter pylori's role in gastritis
Abstract
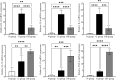
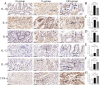
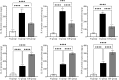
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), known for causing gastric inflammation, gastritis and gastric cancer, prompted our study to investigate the differential expression of cytokines in gastric tissues, which is crucial for understanding H. pylori infection and its potential progression to gastric cancer. Focusing on Il-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-18, and TNF-α, we analysed gene and protein levels to differentiate between H. pylori-infected and non-infected gastritis. We utilised real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) for gene quantification, immunohistochemical staining, and ELISA for protein measurement. Gastric samples from patients with gastritis were divided into three groups: (1) non-gastritis (N-group) group, (2) gastritis without H. pylori infection (G-group), and (3) gastritis with H. pylori infection (GH-group), each consisting of 8 samples. Our findings revealed a statistically significant variation in cytokine expression. Generally, cytokine levels were higher in gastritis, but in H. pylori-infected gastritis, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 levels were lower compared to H. pylori-independent gastritis, while IL-12, IL-18, and TNF-α levels were higher. This distinct cytokine expression pattern in H. pylori-infected gastritis underscores a unique inflammatory response, providing deeper insights into its pathogenesis.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; Cytokines; ELISA; Gastritis; H&E staining; Immunohistochemical staining; Inflammation; RT-qPCR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 04.01.16.035/Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital for climbing talents
- 04.01.16.035/Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital for climbing talents
- CKY2021-28/Chongming District Science and Technology Commission
- CKY2021-28/Chongming District Science and Technology Commission
- 82002588/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

