The effect of physical exercise during radiotherapy on physical performance in patients with head and neck cancer: a trial within cohorts study protocol, the vital study
- PMID: 38561708
- PMCID: PMC10985867
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12172-2
The effect of physical exercise during radiotherapy on physical performance in patients with head and neck cancer: a trial within cohorts study protocol, the vital study
Abstract
Background: During the last decade, twelve studies have been published investigating physical exercise interventions (PEIs) in patients with head and neck cancer (HNC) during radiotherapy (RT), chemoradiation (CRT) or bioradiation (BRT). These studies showed that these PEIs are safe and feasible. However, only two of these studies were randomised clinical trials (RCTs) with a satisfying sample size. Thereby, there is no cost-effectiveness study related to a PEI during RT, CRT or BRT ((C/B)RT) for patients with HNC. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate and compare physical performance, muscle strength, fatigue, quality of life (QoL), body mass index (BMI), nutritional status, physical activity, treatment tolerability, and health care related costs in patients with HNC with and without a 10 week PEI during (C/B)RT.
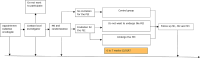
Methods: This study, based on a trial within cohorts (TwiCs) design, will contain a prospective cohort of at least 112 patients. Fifty-six patients will randomly be invited for an experimental 10 week PEI. This PEI consists of both resistance and endurance exercises to optimize physical performance, muscle strength, fatigue, QoL, BMI, nutritional status, physical activity, and treatment tolerability of (C/B)RT. Measurements are at baseline, after 12 weeks, 6 months, and at 12 months. Statistical analyses will be performed for intention-to-treat and instrumental variable analysis.
Discussion: This study seeks to investigate physical, QoL, and economic implications of a PEI. With a substantial sample size, this study attempts to strengthen and expand knowledge in HNC care upon PEI during (C/B)RT. In conclusion, this study is dedicated to provide additional evidence for PEI in patients with HNC during (C/B)RT.
Trial registration: protocol was registered at clinicaltrials.gov with number NCT05988060 on 3 August 2023.
Keywords: Chemo- or bioradiotherapy; Head and neck cancer; Physical exercise intervention; Physical performance; Trial within cohorts; TwiCs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EffEx-HN trial: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial on the EFFectiveness and feasibility of a comprehensive supervised EXercise program during radiotherapy in Head and Neck cancer patients on health-related quality of life.Trials. 2023 Apr 15;24(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07170-x. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37061715 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prophylactic swallowing exercises on dysphagia and quality of life in patients with head and neck cancer receiving (chemo) radiotherapy: the Redyor study, a protocol for a randomized clinical trial.Trials. 2019 Aug 14;20(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3587-x. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31412947 Free PMC article.
-
The PRO-ACTIVE trial protocol: a randomized study comparing the effectiveness of PROphylACTic swallow InterVEntion for patients receiving radiotherapy for head and neck cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 13;21(1):1100. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08826-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34645411 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise interventions for adults with cancer receiving radiation therapy alone.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 13;3(3):CD013448. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013448.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36912791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise for cancer cachexia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3(3):CD010804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010804.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33735441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NKR. Dutch incidence and prevalence head and neck cancer. https://iknl.nl. Accessed 27 Apr 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials