Linkage to HIV care and early retention in HIV care among men in the 'universal test-and-treat' era in a high HIV-burdened district, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
- PMID: 38561736
- PMCID: PMC10985849
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-10736-3
Linkage to HIV care and early retention in HIV care among men in the 'universal test-and-treat' era in a high HIV-burdened district, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the numerous efforts and initiatives, males with HIV are still less likely than women to receive HIV treatment. Across Sub-Saharan Africa, men are tested, linked, and retained in HIV care at lower rates than women, and South Africa is no exception. This is despite the introduction of the universal test-and-treat (UTT) prevention strategy anticipated to improve the uptake of HIV services. The aim of this study was to investigate linkage to and retention in care rates of an HIV-positive cohort of men in a high HIV prevalence rural district in KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa.
Methods: From January 2018 to July 2019, we conducted an observational cohort study in 18 primary health care institutions in the uThukela district. Patient-level survey and clinical data were collected at baseline, 4-months and 12-months, using isiZulu and English REDCap-based questionnaires. We verified data through TIER.Net, Rapid mortality survey (RMS), and the National Health Laboratory Service (NHLS) databases. Data were analyzed using STATA version 15.1, with confidence intervals and p-value of ≤0.05 considered statistically significant.
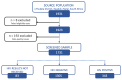
Results: The study sample consisted of 343 male participants diagnosed with HIV and who reside in uThukela District. The median age was 33 years (interquartile range (IQR): 29-40), and more than half (56%; n = 193) were aged 18-34 years. Almost all participants (99.7%; n = 342) were Black African, with 84.5% (n = 290) being in a romantic relationship. The majority of participants (85%; n = 292) were linked to care within three months of follow-up. Short-term retention in care (≤ 12 months) was 46% (n = 132) among men who were linked to care within three months.
Conclusion: While the implementation of the UTT strategy has had positive influence on improving linkage to care, men's access of HIV treatment remains inconsistent and may require additional innovative strategies.
Keywords: HIV treatment; Linkage to care; Men; Retention in care; South Africa.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Barriers and Facilitating Factors to HIV Treatment Among Men in a High-HIV-Burdened District in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: A Qualitative Study.Am J Mens Health. 2022 Sep-Oct;16(5):15579883221120987. doi: 10.1177/15579883221120987. Am J Mens Health. 2022. PMID: 36066024 Free PMC article.
-
Strengthening health system's capacity for linkage to HIV care for adolescent girls and young women and adolescent boys and young men in South Africa (SheS'Cap-Linkage): Protocol for a mixed methods study in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 13;18(2):e0271942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271942. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36780479 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage to HIV Care and Early Retention in Care Rates in the Universal Test-and-Treat Era: A Population-based Prospective Study in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.AIDS Behav. 2023 Apr;27(4):1068-1081. doi: 10.1007/s10461-022-03844-w. Epub 2022 Sep 13. AIDS Behav. 2023. PMID: 36098845 Free PMC article.
-
Provision of HIV testing services and its impact on the HIV positivity rate in the public health sector in KwaZulu-Natal: a ten-year review.SAHARA J. 2024 Dec;21(1):2318797. doi: 10.1080/17290376.2024.2318797. Epub 2024 Feb 19. SAHARA J. 2024. PMID: 38374664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Misreporting of Patient Outcomes in the South African National HIV Treatment Database: Consequences for Programme Planning, Monitoring, and Evaluation.Front Public Health. 2020 Apr 7;8:100. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00100. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32318534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and predictors of virological failure among the people living with HIV on antiretroviral treatment in East Africa: evidence from a systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression of published studies from 2016 to 2023.HIV Res Clin Pract. 2025 Dec;26(1):2490774. doi: 10.1080/25787489.2025.2490774. Epub 2025 Apr 11. HIV Res Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 40219653
-
Interventions for reaching men to improve HIV Testing Services in sub-Saharan Africa: A narrative review.Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2025 Jun 25;17(1):e1-e13. doi: 10.4102/phcfm.v17i1.4869. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2025. PMID: 40599031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends and factors associated with retention in HIV care among men living with HIV in a peri-urban primary care facility in central Uganda: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 21;25(1):1876. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23161-w. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40399890 Free PMC article.
-
Trajectories and predictors of HIV care retention among individuals receiving ART in rural South Africa: a group-based trajectory modelling analysis.J Glob Health. 2025 Jul 1;15:04187. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04187. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40587184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS . Blind spot: reaching out to men and boys. Addressing a blind spot in the response to HIV. Geneva, Switzerland: UNAIDS; 2017.
-
- Staveteig S, Wang S, Head SK, Bradley SE, Nybro E. Demographic patterns of HIV testing uptake in sub-saharan Africa. ICF International Calverton, MD; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

