Transcriptional regulation of cancer stem cell: regulatory factors elucidation and cancer treatment strategies
- PMID: 38561775
- PMCID: PMC10986082
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03021-y
Transcriptional regulation of cancer stem cell: regulatory factors elucidation and cancer treatment strategies
Abstract
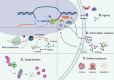
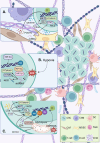
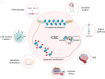
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) were first discovered in the 1990s, revealing the mysteries of cancer origin, migration, recurrence and drug-resistance from a new perspective. The expression of pluripotent genes and complex signal regulatory networks are significant features of CSC, also act as core factors to affect the characteristics of CSC. Transcription is a necessary link to regulate the phenotype and potential of CSC, involving chromatin environment, nucleosome occupancy, histone modification, transcription factor (TF) availability and cis-regulatory elements, which suffer from ambient pressure. Especially, the expression and activity of pluripotent TFs are deeply affected by both internal and external factors, which is the foundation of CSC transcriptional regulation in the current research framework. Growing evidence indicates that regulating epigenetic modifications to alter cancer stemness is effective, and some special promoters and enhancers can serve as targets to influence the properties of CSC. Clarifying the factors that regulate CSC transcription will assist us directly target key stem genes and TFs, or hinder CSC transcription through environmental and other related factors, in order to achieve the goal of inhibiting CSC and tumors. This paper comprehensively reviews the traditional aspects of transcriptional regulation, and explores the progress and insights of the impact on CSC transcription and status through tumor microenvironment (TME), hypoxia, metabolism and new meaningful regulatory factors in conjunction with the latest research. Finally, we present opinions on omnidirectional targeting CSCs transcription to eliminate CSCs and address tumor resistance.
Keywords: CSC; DNA elements; Signaling pathways,epigenetics; TF; TME; Transcription regulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(19):8721-8743. doi: 10.7150/thno.41648. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32754274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine-Induced Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Cell Transition and Cancer Stem Cell Generation.Cells. 2019 Sep 25;8(10):1143. doi: 10.3390/cells8101143. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31557902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional factors targeting in cancer stem cells for tumor modulation.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Jan;88:123-137. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.12.010. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 36603792 Review.
-
Exploiting transcription factors to target EMT and cancer stem cells for tumor modulation and therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2024 May;100:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.03.002. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Semin Cancer Biol. 2024. PMID: 38503384 Review.
-
Regulation and signaling pathways in cancer stem cells: implications for targeted therapy for cancer.Mol Cancer. 2023 Oct 18;22(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01877-w. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37853437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights on Bmi-1 therapeutic targeting in head and neck cancers.Oncol Res. 2025 Jan 16;33(2):301-307. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.053764. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 39866230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt signaling pathways in biology and disease: mechanisms and therapeutic advances.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Apr 4;10(1):106. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02142-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40180907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of G1 phase kinetics on the acquisition of stemness in cancer cells: the critical role of cyclin D.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 14;52(1):230. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10351-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39951181 Review.
-
Nanomaterials targeting cancer stem cells to overcome drug resistance and tumor recurrence.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 6;15:1499283. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1499283. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40548119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the role of cancer stem cells in digestive tract tumors: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Jul;67(1):61. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5767. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40576138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Velten L, Story BA, Hernández-Malmierca P, Raffel S, Leonce DR, Milbank J, Paulsen M, Demir A, Szu-Tu C, Frömel R, Lutz C, Nowak D, Jann J-C, Pabst C, Boch T, Hofmann W-K, Müller-Tidow C, Trumpp A, Haas S, Steinmetz LM.'Identification of leukemic and pre-leukemic stem cells by clonal tracking from single-cell transcriptomics'. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1366. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

