Liquid biopsy techniques and lung cancer: diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation
- PMID: 38561776
- PMCID: PMC10985944
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03026-7
Liquid biopsy techniques and lung cancer: diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation
Abstract
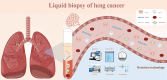
Lung cancer stands as the most prevalent form of cancer globally, posing a significant threat to human well-being. Due to the lack of effective and accurate early diagnostic methods, many patients are diagnosed with advanced lung cancer. Although surgical resection is still a potential means of eradicating lung cancer, patients with advanced lung cancer usually miss the best chance for surgical treatment, and even after surgical resection patients may still experience tumor recurrence. Additionally, chemotherapy, the mainstay of treatment for patients with advanced lung cancer, has the potential to be chemo-resistant, resulting in poor clinical outcomes. The emergence of liquid biopsies has garnered considerable attention owing to their noninvasive nature and the ability for continuous sampling. Technological advancements have propelled circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), extracellular vesicles (EVs), tumor metabolites, tumor-educated platelets (TEPs), and tumor-associated antigens (TAA) to the forefront as key liquid biopsy biomarkers, demonstrating intriguing and encouraging results for early diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of lung cancer. This review provides an overview of molecular biomarkers and assays utilized in liquid biopsies for lung cancer, encompassing CTCs, ctDNA, non-coding RNA (ncRNA), EVs, tumor metabolites, TAAs and TEPs. Furthermore, we expound on the practical applications of liquid biopsies, including early diagnosis, treatment response monitoring, prognostic evaluation, and recurrence monitoring in the context of lung cancer.
Keywords: Circulating tumor DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Extracellular vesicles; Liquid biopsy; Lung cancer; Noncoding RNAs; Tumor metabolite; Tumor-associated antigens; Tumor-educated platelet.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F, Global Cancer Statistics 2020. : GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries, CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 71 (2021) 209–4910.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Dou Y, Sui Z, Cheng H, Liu X, Wang Q, Xu M, et al. Upregulated miRNA-182-5p expression in tumor tissue and peripheral blood samples from patients with non-small cell lung cancer is associated with downregulated caspase 2 expression. Experimental Therapeutic Med. 2020;19:603–10. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

