Characterization of feline-originated probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus CACC612 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CACC789 and and evaluation of their host response
- PMID: 38561808
- PMCID: PMC10983674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-03975-3
Characterization of feline-originated probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus CACC612 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CACC789 and and evaluation of their host response
Abstract
Background: Probiotics are beneficial for animal health and new potential probiotics need to be characterized for their prospective use in improving animal health. In this study, 32 bacterial strains were isolated from a Norwegian forest cat (castrated, 12 years old) and a Persian cat (castrated, 10 years old), which were privately owned and had indoor access.
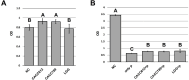
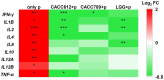
Results: Lactobacillus rhamnosus CACC612 (CACC612) and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CACC789 (CACC789) were selected as potential probiotics; characterization of the two strains showed equivalent acid tolerance, similar cell adhesion rates on the HT-29 monolayer cell line, and superior bile tolerance compared to Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG). Subsequently, they exhibited inhibitory effects against a broad spectrum of pathogenic bacteria, including E. coli (KCTC 2617), Salmonella Derby (NCCP 12,238), Salmonella Enteritidis (NCCP 14,546), Salmonella Typhimurium (NCCP 10,328), Clostridium difficile JCM 1296T. From evaluating host effects, the viability of the feline macrophage cell line (Fcwf-4) increased with the treatment of CACC612 or CACC789 (P < 0.05). The induced expression of immune-related genes such as IFN-γ, IL1β, IL2, IL4, and TNF-α by immune stimulation was significantly attenuated by the treatment of CACC612 or CACC789 (P < 0.05). When 52 clinical factors of sera from 21 healthy cats were analyzed using partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), the animals were obviously clustered before and after feeding with CACC612 or CACC789. In addition, hemoglobin and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) significantly increased after CACC612 feeding (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: In this study, feline-originated probiotics were newly characterized and their potentially probiotic effects were evaluated. These results contribute to our understanding of the functional effects of feline-derived probiotics and support their industrial applications.
Keywords: Animal health; Feline; Immune; Probiotic characterization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- FAO/WHO. Evaluation of health and nutritional properties of powder milk and live lactic acid bacteria. : FAO Rome; 2001: 1–34.
-
- Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11(8):506–14. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

