Epigenetic programming of stochastic olfactory receptor choice
- PMID: 38562011
- PMCID: PMC11003729
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.23593
Epigenetic programming of stochastic olfactory receptor choice
Abstract
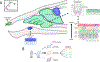
The mammalian sense of smell relies upon a vast array of receptor proteins to detect odorant compounds present in the environment. The proper deployment of these receptor proteins in olfactory sensory neurons is orchestrated by a suite of epigenetic processes that remodel the olfactory genes in differentiating neuronal progenitors. The goal of this review is to elucidate the central role of gene regulatory processes acting in neuronal progenitors of olfactory sensory neurons that lead to a singular expression of an odorant receptor in mature olfactory sensory neurons. We begin by describing the principal features of odorant receptor gene expression in mature olfactory sensory neurons. Next, we delineate our current understanding of how these features emerge from multiple gene regulatory mechanisms acting in neuronal progenitors. Finally, we close by discussing the key gaps in our understanding of how these regulatory mechanisms work and how they interact with each other over the course of differentiation.
Keywords: chemosensory neurons; chromatin; gene expression; heterochromatin; olfaction; olfactory receptors; vomeronasal organ.
© 2024 The Authors. genesis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How smell develops.Nat Neurosci. 2001 Nov;4 Suppl:1192-8. doi: 10.1038/nn751. Nat Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11687829 Review.
-
Mechanisms controlling diversification of olfactory sensory neuron classes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3263-3274. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2512-2. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28357469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Singular expression of olfactory receptor genes.Cell. 2013 Oct 10;155(2):274-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.032. Cell. 2013. PMID: 24120129 Review.
-
The extremely broad odorant response profile of mouse olfactory sensory neurons expressing the odorant receptor MOR256-17 includes trace amine-associated receptor ligands.Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Mar;43(5):608-17. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13153. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Eur J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26666691 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal Odorant Receptors Mediate Axon Targeting.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 24;29(13):4334-4348.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.099. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31875544 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In mice, discrete odors can selectively promote the neurogenesis of sensory neuron subtypes that they stimulate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 11:2024.02.10.579748. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.10.579748. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jun 18;13:RP96152. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96152. PMID: 38405728 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
In mice, discrete odors can selectively promote the neurogenesis of sensory neuron subtypes that they stimulate.Elife. 2025 Jun 18;13:RP96152. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96152. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40531183 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Rearrangement of the Olfactory Epithelium in Male Baikal Yellowfin Sculpins Across the Reproductive Period.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 10;14(2):179. doi: 10.3390/biology14020179. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes IHA, Ibarra-Soria X, Fitzgerald S, Gonzalez JM, Davidson C, Hardy MP, Manthravadi D, Van Gerven L, Jorissen M, Zeng Z, Khan M, Mombaerts P, Harrow J, Logan DW, & Frankish A (2020). Expert curation of the human and mouse olfactory receptor gene repertoires identifies conserved coding regions split across two exons. BMC Genomics, 21(1), 196. 10.1186/s12864-020-6583-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

