Correlation Between ImageJ and Conventional Manual Scoring Methods for Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Immuno-Histochemically Stained Sections
- PMID: 38562094
- PMCID: PMC10989033
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338241242635
Correlation Between ImageJ and Conventional Manual Scoring Methods for Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Immuno-Histochemically Stained Sections
Abstract
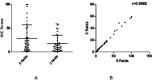
Background: One of the most frequently used methods for quantifying PD-L1 (programmed cell death-ligand 1) expression in tumor tissue is IHC (immunohistochemistry). This may predict the patient's response to anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapy in cancer. Methods: ImageJ software was used to score IHC-stained sections for PD-L1 and compare the results with the conventional manual method. Results: In diffuse large B cell lymphoma, no significant difference between the scores obtained by the conventional method and ImageJ scores obtained using the option "RGB" or "Brightness/Contrast." On the other hand, a significant difference was found between the conventional and HSB scoring methods. ImageJ faced some challenges in analyzing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma tissues because of tissue heterogenicity. A significant difference was found between the conventional and ImageJ scores using HSB or RGB but not with the "Brightness/Contrast" option. Scores obtained by ImageJ analysis after taking images using 20 × objective lens gave significantly higher readings compared to 40 × magnification. A significant difference between camera-captured images' scores and scanner whole slide images' scores was observed. Conclusion: ImageJ can be used to score homogeneous tissues. In the case of highly heterogeneous tissues, it is advised to use the conventional method rather than ImageJ scoring.
Keywords: ImageJ; PD-L1; immunohistochemistry; manual scoring; scoring.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


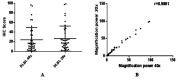

References
-
- Mane DR, Kale AD, Belaldavar C. Validation of immunoexpression of tenascin-C in oral precancerous and cancerous tissues using ImageJ analysis with novel immunohistochemistry profiler plugin: an immunohistochemical quantitative analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017;21(2):211. DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_234_16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

