Assessment of knowledge and perceptions of human papillomavirus vaccine and its determinants among women who have eligible daughters in Debre Berhan City, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38562169
- PMCID: PMC10982310
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1348288
Assessment of knowledge and perceptions of human papillomavirus vaccine and its determinants among women who have eligible daughters in Debre Berhan City, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Globally, cervical cancer(CC) is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the leading cause of CC. Persistent infection with HPV accounts for 90% of all CC cases. The human papillomavirus vaccine has the great potential to prevent HPV-related infections for millions of women and men. The current study aimed to assess knowledge and perceptions towards the HPV vaccine and its determinants among women who have eligible daughters in Debre Berhan City, Ethiopia.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from April 2, 2023, to May 15, 2023. A multistage sampling procedure was used to recruit 607 women participants. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize socio-demographic data. Univariable and multivariable binary logistic regression analyses were performed to measure the associations between the dependent and independent variables. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
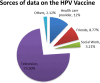
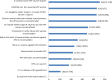
Results: More than three-fourths of the participants, 479 individuals (80%) were currently married, and 243(40.1%) had a diploma or higher education level. Of 456(75.12) participants reported, they had information about cervical cancer. For 449(73.9%) of the participants, television was the main evidence. The majority of 352(59.99%) participants knew the HPV vaccine could be offered to a female child aged 9-14 years old. Only 215(35.4%) participants think the HPV vaccine was safe and effective. Women who had a degree and above educational level were about 9 times more likely to have good knowledge about the HPV vaccine than study participants who did not read and write (AOR=9.21; 95% CI=2.82-12.16; p=0.004). Women who did not have information about the HPV vaccine before this study were about 80% less likely to have a positive perception of the HPV vaccine than participants who had earlier information about the HPV vaccine (AOR=0.8; 95%CI=0.63-0.49; P=003).
Conclusion: Women had poor knowledge and perceptions about the HPV vaccine. Maternal marital status, age, and having information about the HPV vaccine were the only predictors of women's knowledge of the HPV vaccine.
Keywords: cervical cancer; human papilloma virus; human papilloma virus vaccine; knowledge; perceptions; women.
Copyright © 2024 Tsige, Ayenew and Ayele.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Knowledge and Attitudes Among Adolescent School Girls in Debre Berhan City, Ethiopia: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;8(2):e70506. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70506. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39995791 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and willingness of parents towards child girl HPV vaccination in Debre Tabor Town, Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study.Reprod Health. 2022 Jun 10;19(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12978-022-01444-4. Reprod Health. 2022. PMID: 35689288 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Attitude Towards Human Papillomavirus Vaccine and Associated Factors Among Mothers Who Have Eligible Daughters in Debre Markos Town, Northwest Ethiopia.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Mar 3;15:781-793. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S352440. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35264861 Free PMC article.
-
Male support for cervical cancer screening in Debre Berhan City Ethiopia a community based cross sectional survey.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 7;14(1):18302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69439-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39112655 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude, and uptake of human papillomavirus vaccine among adolescent schoolgirls in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2023 May 20;23(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02412-1. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37210492 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Knowledge and Attitudes Among Adolescent School Girls in Debre Berhan City, Ethiopia: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;8(2):e70506. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70506. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39995791 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

