The Association Between Epidermal Growth Factor rs3756261 A/G Gene Polymorphism and the Risk of Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Chinese Han Population
- PMID: 38562211
- PMCID: PMC10982052
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S448976
The Association Between Epidermal Growth Factor rs3756261 A/G Gene Polymorphism and the Risk of Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Chinese Han Population
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a potent pro-angiogenic molecule promoting the angiogenic phenotype of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Studies demonstrated that EGF rs3756261 polymorphism was associated with the risk of inflammatory diseases, but not including AS.
Methods: To investigate the association between EGF rs3756261 polymorphism and the risk of AS, we genotyped the EGF rs3756261 polymorphism in 208 patients with AS and 412 controls in a Chinese Han population using a custom-by-design 48-Plex SNP scanTM Kit. The serum EGF levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 208 AS patients and 412 controls.
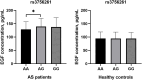
Results: Our data indicated that EGF rs3756261 polymorphism was associated with an increased risk of AS in the Chinese Han population. Stratified analyses indicated that the EGF rs3756261 polymorphism elevated the risk of AS among the males, smokers, drinkers and those aged <30 years. In addition, the EGF rs3756261 polymorphism was related to increased CRP and HLA-B27 levels in AS patients. Next, we found that the average serum levels of EGF were significantly higher in AS patients compared with controls. Meanwhile, EGF serum levels were significantly higher in AG genotype carriers when compared with AA genotype carriers in AS patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study indicated that EGF rs3756261 polymorphism was associated with the risk of AS and EGF serum levels in a Chinese Han population.
Keywords: EGF; ankylosing spondylitis; case–control study; rs3756261 polymorphism; serum levels.
© 2024 Zhang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between C-reactive protein gene variant and treatment efficacy of etanercept in ankylosing spondylitis patients receiving hip arthroplasty.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Aug;34(8):e23343. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23343. Epub 2020 Apr 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32311164 Free PMC article.
-
EGF rs11568835 G/A polymorphism is associated with increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis.Biomarkers. 2014 Nov;19(7):563-6. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2014.946450. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Biomarkers. 2014. PMID: 25089940
-
Associations of the IL-1B level, IL-1A and IL-1B gene polymorphisms and ankylosing spondylitis risk in a Chinese Han population.Cytokine. 2020 Feb;126:154918. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154918. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31726259
-
Associations of the VEGF level, VEGF rs2010963 G/C gene polymorphism and ankylosing spondylitis risk in a Chinese Han population.Immunol Lett. 2016 Nov;179:56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27637764
-
Association study of ankylosing spondylitis and polymorphisms in ERAP1 gene in Zhejiang Han Chinese population.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Feb;36(2):243-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3350-x. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26350268
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous