Associations of anxiety and depression with restless leg syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38562425
- PMCID: PMC10982394
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1366839
Associations of anxiety and depression with restless leg syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The levels of anxiety and depression among patients with restless leg syndrome (RLS) are controversial. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the levels of depression and anxiety among individuals with RLS with those of healthy controls.
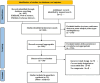
Methods: We conducted an extensive electronic search of the PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases from their inception dates to 20 June 2023. Studies presenting data on depression and anxiety in individuals with RLS were included, and a comprehensive meta-analysis was performed.
Results: Twenty-one studies matched the inclusion criteria. Significantly more depressive symptoms were present in the individuals with RLS than in those without RLS, as measured by the Beck Depression Inventory [mean difference (MD) = 6.58, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 5.54-7.62, p < 0.01; heterogeneity I2 = 0%, p = 0.99]. Similarly, the results from the Beck Anxiety Inventory indicated that there were significantly more pronounced anxiety symptoms in the individuals with RLS than in those without RLS (MD = 9.30, 95%CI = 7.65-10.94, p < 0.01; heterogeneity I2 = 0%, p = 0.92). The other anxiety and depression scales also yielded statistically significant results. Significant heterogeneity was observed in the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, with the primary contributing factor probably being the scoring criteria of the scales.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis found that the levels of depression and anxiety symptoms were significantly higher in individuals with RLS than in their healthy counterparts.Systematic review registration:https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023410364, (identifier CRD42023410364).
Keywords: anxiety; depression; mental health; meta-analysis; restless legs syndrome.
Copyright © 2024 An, Sun, Yuan, Wu and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG, Walters AS, Winkelman JW, et al. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: updated international restless legs syndrome study group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria-history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. (2014) 15:860–73. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2014.03.025, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

