Comparison of the Application of Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer and Jet Nebulizer in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 38562440
- PMCID: PMC10984201
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S452191
Comparison of the Application of Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer and Jet Nebulizer in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To comparison of the application of Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer and Jet Nebulizer in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Research methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statements. The primary outcome measures analyzed included: The amount of inhaler in the urine sample at 30 minutes after inhalation therapy (USAL0.5), The total amount of inhaler in urine sample within 24 hours (USAL24), Aerosol emitted, Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), Forced vital capacity (FVC).
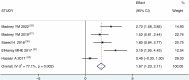
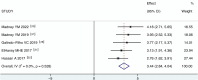
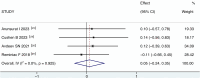
Results: Ten studies were included with a total of 314 study participants, including 157 subjects in the VMN group and 157 subjects in the JN group. The data analysis results of USAL0.5, MD (1.88 [95% CI, 0.95 to 2.81], P = 0.000), showed a statistically significant difference. USAL24, MD (1.61 [95% CI, 1.14 to 2.09], P = 0.000), showed a statistically significant difference. The results of aerosol emitted showed a statistically significant difference in MD (3.44 [95% CI, 2.84 to 4.04], P = 0.000). The results of FEV1 showed MD (0.05 [95% CI, -0.24 to 0.35], P=0.716), the results were not statistically significant. The results of FVC showed MD (0.11 [95% CI, -0.18 to 0.41], P=0.459), the results were not statistically significant. It suggests that VMN is better than JN and provides higher aerosols, but there is no difference in improving lung function between them.
Conclusion: VMN is significantly better than JN in terms of drug delivery and utilization in the treatment of patients with COPD. However, in the future use of nebulizers, it is important to select a matching nebulizer based on a combination of factors such as mechanism of action of the nebulizer, disease type and comorbidities, ventilation strategies and modes, drug formulations, as well as cost-effectiveness, in order to achieve the ideal treatment of COPD.
Keywords: aerosol; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; jet nebulizers; meta-analysis; vibrating mesh nebulizers.
© 2024 Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Efficacy and safety of ensifentrine in treatment of COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666251347775. doi: 10.1177/17534666251347775. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40538231 Free PMC article.
-
Tiotropium versus placebo for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;(7):CD009285. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009285.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 21;(7):CD009285. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009285.pub3. PMID: 22786525 Updated.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(19):iii-iv, 1-360. doi: 10.3310/hta12190. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18485271
-
Aerosol Delivery to Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Tracheostomized Adult Model With and Without Humidification.Respir Care. 2024 Jun 28;69(7):847-853. doi: 10.4187/respcare.11495. Respir Care. 2024. PMID: 38485144 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recalibrating Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Nebulizers versus Inhalers for Maintenance Therapy in COPD: Past as Prologue.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Nov 28;19:2571-2586. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S491275. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 39629181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aerosol Delivery With High-Frequency Assisted Airway Clearance Therapy in an Adult Airway and Lung Model: A Perfect Marriage?Respir Care. 2024 Sep 26;69(10):1345-1346. doi: 10.4187/respcare.12428. Respir Care. 2024. PMID: 39327027 No abstract available.
-
Challenges and Opportunities in COPD Management in Latin America: A Review of Inhalation Therapies and Advanced Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 11;16(10):1318. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101318. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

