Padi6 expression patterns in buffalo oocytes and preimplantation embryos
- PMID: 38562607
- PMCID: PMC10984561
- DOI: 10.1590/1984-3143-AR2023-0146
Padi6 expression patterns in buffalo oocytes and preimplantation embryos
Abstract
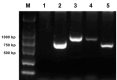
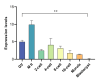
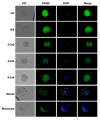
The subcortical maternal complex, which consists of maternal-effect genes, plays a crucial role in the development of oocytes and preimplantation embryo until the activation of the zygote genome. One such gene, known as peptidyl-arginine deiminase VI (Padi6), is involved in the oocyte maturation, fertilization and embryonic development. However, the precise function of Padi6 gene in buffalo is still unclear and requires further investigation. In this study, the sequence, mRNA and protein expression patterns of Padi6 gene were analyzed in oocytes, preimplantation embryos and somatic tissues of buffalo. The coding sequence of gene was successfully cloned and characterized. Real-time quantitative PCR results indicated an absence of Padi6 transcripts in somatic tissues. Notably, the expression levels of Padi6 in oocytes showed an increased from the germinal vesicle stage to metaphase II stage, followed by a rapid decrease during the morula and blastocyst stages. Immunofluorescence analysis confirmed these findings, revealing a noticeable decline in protein expression levels. Our research provides the initial comprehensive expression profile of Padi6 in buffalo oocytes and preimplantation embryos, serving as a solid foundation for further investigations into the functionality of maternal-effect genes in buffalo.
Keywords: Padi6; immunofluorescence; maternal-effect genes; oocyte; preimplantation embryo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nlrp5 and Tle6 expression patterns in buffalo oocytes and pre-implantation embryos.Reprod Domest Anim. 2022 May;57(5):481-488. doi: 10.1111/rda.14084. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Reprod Domest Anim. 2022. PMID: 35044003
-
A maternal-effect Padi6 variant causes nuclear and cytoplasmic abnormalities in oocytes, as well as failure of epigenetic reprogramming and zygotic genome activation in embryos.Genes Dev. 2024 Mar 22;38(3-4):131-150. doi: 10.1101/gad.351238.123. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 38453481 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Cpt1b and Cpt2 gene expression in mouse antral oocytes and in preimplantation embryos.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;105(2-4):215-21. doi: 10.1159/000078191. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15237209
-
TEAD4 regulates trophectoderm differentiation upstream of CDX2 in a GATA3-independent manner in the human preimplantation embryo.Hum Reprod. 2022 Jul 30;37(8):1760-1773. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac138. Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35700449
-
PADI6: What we know about the elusive fifth member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023 Nov 20;378(1890):20220242. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0242. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37778376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chavanas S, Mechin MC, Takahara H, Kawada A, Nachat R, Serre G, Simon M. Comparative analysis of the mouse and human peptidylarginine deiminase gene clusters reveals highly conserved non-coding segments and a new human gene, PADI6. Gene. 2004;330:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2003.12.038. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Esposito G, Vitale AM, Leijten FPJ, Strik AM, Koonen-Reemst AMCB, Yurttas P, Robben TJAA, Coonrod S, Gossen JA. Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) 6 is essential for oocyte cytoskeletal sheet formation and female fertility. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;273(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A. In: The proteomics protocols handbook. Walker JM, editor. Nova Jersey: Humana Press; 2005. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. (Springer Protocols Handbooks). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
