This is a preprint.
Validation of Enhancer Regions in Primary Human Neural Progenitor Cells using Capture STARR-seq
- PMID: 38562832
- PMCID: PMC10983874
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.14.585066
Validation of Enhancer Regions in Primary Human Neural Progenitor Cells using Capture STARR-seq
Update in
-
A map of enhancer regions in primary human neural progenitor cells using capture STARR-seq.Genome Res. 2025 Aug 1;35(8):1887-1901. doi: 10.1101/gr.279584.124. Genome Res. 2025. PMID: 40645663
Abstract
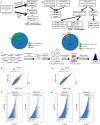
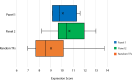
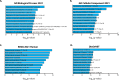
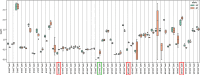
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and expression analyses implicate noncoding regulatory regions as harboring risk factors for psychiatric disease, but functional characterization of these regions remains limited. We performed capture STARR-sequencing of over 78,000 candidate regions to identify active enhancers in primary human neural progenitor cells (phNPCs). We selected candidate regions by integrating data from NPCs, prefrontal cortex, developmental timepoints, and GWAS. Over 8,000 regions demonstrated enhancer activity in the phNPCs, and we linked these regions to over 2,200 predicted target genes. These genes are involved in neuronal and psychiatric disease-associated pathways, including dopaminergic synapse, axon guidance, and schizophrenia. We functionally validated a subset of these enhancers using mutation STARR-sequencing and CRISPR deletions, demonstrating the effects of genetic variation on enhancer activity and enhancer deletion on gene expression. Overall, we identified thousands of highly active enhancers and functionally validated a subset of these enhancers, improving our understanding of regulatory networks underlying brain function and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Kevin P. White is a shareholder of Tempus Labs, Inc. and Provaxus, Inc. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A map of enhancer regions in primary human neural progenitor cells using capture STARR-seq.Genome Res. 2025 Aug 1;35(8):1887-1901. doi: 10.1101/gr.279584.124. Genome Res. 2025. PMID: 40645663
-
Analysis of biased allelic enhancer activity of schizophrenia-linked common variants.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 10;8(1):1034. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08456-3. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40640362 Free PMC article.
-
Coding and noncoding variants in EBF3 are involved in HADDS and simplex autism.Hum Genomics. 2021 Jul 13;15(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s40246-021-00342-3. Hum Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34256850 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (HHS Publication No. PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56, 2021).
-
- Merikangas K. R., He J. P., Burstein M., Swanson S. A., Avenevoli S., Cui L., Benjet C., Georgiades K., Swendsen J., Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in U.S. adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication--Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49, 980–989 (2010). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
