This is a preprint.
Auto-sumoylation of the Ubc9 E2 SUMO-conjugating Enzyme Extends Cellular Lifespan
- PMID: 38562857
- PMCID: PMC10984013
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4016606/v1
Auto-sumoylation of the Ubc9 E2 SUMO-conjugating Enzyme Extends Cellular Lifespan
Update in
-
Auto-sumoylation of the yeast Ubc9 E2 SUMO-conjugating enzyme extends cellular lifespan.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 20;16(1):3735. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58925-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40254622 Free PMC article.
Abstract
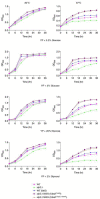
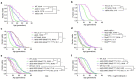
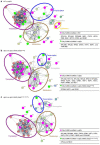
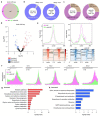
Calorie restriction (CR) provides anti-aging benefits through diverse processes, such as reduced metabolism and growth and increased mitochondrial activity. Although controversy still exists regarding CR-mediated lifespan effects, many researchers are seeking interventions that mimic the effects of CR. Yeast has proven to be a useful model system for aging studies, including CR effects. We report here that yeast adapted through in vitro evolution to the severe cellular stress caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO-specific protease exhibit both enhanced growth rates and replicative lifespan, and they have altered gene expression profiles similar to those observed in CR. Notably, in certain evolved ulp2Δ lines, a dramatic increase in the auto-sumoylation of Ubc9 E2 SUMO-conjugating enzyme results in altered regulation of multiple targets involved in energy metabolism and translation at both transcriptional and post-translational levels. This increase is essential for the survival of aged cells and CR-mediated lifespan extension. Thus, we suggest that high Ubc9 auto-sumoylation exerts potent anti-aging effects by promoting efficient energy metabolism-driven improvements in cell replication abilities. This potential could be therapeutically explored for the development of novel CR-mimetic strategies.
Keywords: SUMO; Ubc9; calorie restriction; energy metabolism; lifespan.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

