A homozygous SP7/OSX mutation causes osteogenesis and dentinogenesis imperfecta with craniofacial anomalies
- PMID: 38562913
- PMCID: PMC10984723
- DOI: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae026
A homozygous SP7/OSX mutation causes osteogenesis and dentinogenesis imperfecta with craniofacial anomalies
Abstract
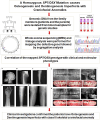
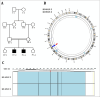
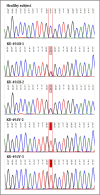
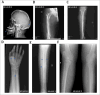
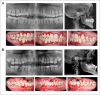
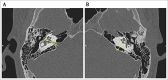
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a heterogeneous spectrum of hereditary genetic disorders that cause bone fragility, through various quantitative and qualitative defects of type 1 collagen, a triple helix composed of two α1 and one α2 chains encoded by COL1A1 and COL1A2, respectively. The main extra-skeletal manifestations of OI include blue sclerae, opalescent teeth, and hearing impairment. Moreover, multiple genes involved in osteoblast maturation and type 1 collagen biosynthesis are now known to cause recessive forms of OI. In this study a multiplex consanguineous family of two affected males with OI was recruited for genetic screening. To determine the causative, pathogenic variant(s), genomic DNA from two affected family members were analyzed using whole exome sequencing, autozygosity mapping, and then validated with Sanger sequencing. The analysis led to the mapping of a homozygous variant previously reported in SP7/OSX, a gene encoding for Osterix, a transcription factor that activates a repertoire of genes involved in osteoblast and osteocyte differentiation and function. The identified variant (c.946C > T; p.Arg316Cys) in exon 2 of SP7/OSX results in a pathogenic amino acid change in two affected male siblings and develops OI, dentinogenesis imperfecta, and craniofacial anomaly. On the basis of the findings of the present study, SP7/OSX:c. 946C > T is a rare homozygous variant causing OI with extra-skeletal features in inbred Arab populations.
Keywords: SP7/OSX gene; conductive hearing loss; consanguinity; craniofacial anomalies; dentinogenesis imperfecta; osteogenesis imperfecta.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel variant in Sp7/Osx associated with recessive osteogenesis imperfecta with bone fragility and hearing impairment.Bone. 2018 May;110:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.01.031. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Bone. 2018. PMID: 29382611
-
Analysis of the clinical and genetic characteristics of a Chinese family with osteogenesis imperfecta type I.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Sep;10(9):e2019. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2019. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 35855543 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 collagenopathy presenting with a Russell-Silver phenotype.Am J Med Genet A. 2011 Jun;155A(6):1414-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33998. Epub 2011 May 12. Am J Med Genet A. 2011. PMID: 21567925
-
[Genetic basis for skeletal disease. Osteogenesis imperfecta and genetic abnormalities].Clin Calcium. 2010 Aug;20(8):1190-5. Clin Calcium. 2010. PMID: 20675929 Review. Japanese.
-
Rare splicing mutation in COL1A1 gene identified by whole exomes sequencing in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta type I followed by prenatal diagnosis: A case report and review of the literature.Gene. 2020 May 30;741:144565. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144565. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32165296
Cited by
-
Osteoclast-independent osteocyte dendrite defects in mice bearing the osteogenesis imperfecta-causing Sp7 R342C mutation.Bone Res. 2025 Jul 19;13(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00440-1. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40683889 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular crosstalk in SP7-mediated osteogenesis: Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2025 Jun;11(2):31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2025.04.003. Epub 2025 May 13. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2025. PMID: 40677780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the Genetics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta.Calcif Tissue Int. 2024 Dec;115(6):891-914. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01266-5. Epub 2024 Aug 11. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024. PMID: 39127989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel pathogenic variants of DNAH5 associated with clinical and genetic spectra of primary ciliary dyskinesia in an Arab population.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 10;15:1396797. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1396797. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39045318 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Skeletal Development and Maintenance by Runx2 and Sp7.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 20;25(18):10102. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810102. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

