Contrast arthrography of the equine temporomandibular joint
- PMID: 38562918
- PMCID: PMC10983794
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1368131
Contrast arthrography of the equine temporomandibular joint
Abstract
Background: Disorders of the equine temporomandibular joint (TMJ) cause clinical problems and detailed investigations of this joint are becoming more common. Specialist radiographic projections have the potential to highlight osseous abnormalities; however, the ability to assess the intra-articular soft tissue structures is currently limited to computed tomography (with, or without contrast enhancement) or magnetic resonance imaging. Both modalities are expensive and not readily accessible.
Objective: To develop a technique of contrast arthrography of both compartments of the equine TMJ in cadavers and then perform the refined technique in three living horses as a proof-of-principle.
Study design: A descriptive, experimental, study.
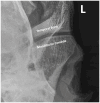
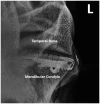
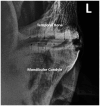
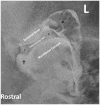
Methods: Contrast arthrography of the discomandibular and discotemporal joint compartments of both TMJs was performed in 12 cadaveric equine heads using needles placed in the caudal pouches of the respective joint compartments. Radiographs were taken using previously published techniques, repeated with the mouth open and after air had been injected into the joints, to perform a double-contrast study. The TMJs of three healthy horses were subsequently examined to determine the validity of the procedure in live animals.
Results: Single and double-contrast arthrography allowed delineation of the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the intra-articular disc in addition to filling the rostral and caudal joint pouches of the independent joint compartments. Contrast extravasation was common, and in two instances iatrogenic disc penetration resulted in the false diagnosis of pathologic disc perforation. The techniques were well tolerated in all three live horses.
Main limitations: Low number of horses.
Conclusion: Contrast arthrography allows interpretation of intra-articular soft tissue structures, but caution is advised in diagnosing intra-articular disc perforation. Even with experience, accessing the discomandibular joint can be challenging.
Keywords: TMJ; horse; imaging; intra-articular disc; radiography.
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Reisbig and Carmalt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Frequency of Communication Between the Synovial Compartments of the Equine Temporomandibular Joint: A Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographic Assessment.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Oct 25;8:753983. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.753983. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34760960 Free PMC article.
-
The Equine Temporomandibular Joint: Comparisons Between Standard and Needle Arthroscopic Examination of Cadaver Specimens and Standing Horses.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Apr 26;9:876041. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.876041. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35558885 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic anatomy of the equine temporomandibular joint.Vet Surg. 2001 Nov-Dec;30(6):564-71. doi: 10.1053/jvet.2001.28438. Vet Surg. 2001. PMID: 11704953
-
Imaging of the temporomandibular joint.Radiol Clin North Am. 1990 Sep;28(5):1019-31. Radiol Clin North Am. 1990. PMID: 2201998 Review.
-
[Imaging of the temporomandibular joint].Rev Belge Med Dent (1984). 1997;52(1):283-303. Rev Belge Med Dent (1984). 1997. PMID: 9709805 Review. French.
References
-
- Levring Jäghagen E, Ahlqvist J. Arthrography of the temporomandibular joint: main diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Clin Dent Rev. (2020) 4:2. doi: 10.1007/s41894-019-0064-6 - DOI
-
- Levring Jäghagen E, Ahlqvist J. Arthrography of the temporomandibular joint and arthrography-guided steroid treatment In: Rozylo-Kalinowska I, Orhan K, editors. Imaging of the temporomandibular joint. Cham: Springer; (2019). 301–22.
-
- Arnaudow M, Haage H, Pflaum I. Die doppelkontrast arthrographie des kiefergelenkes. Dtsch Zahnartztl Z. (1968) 23:390–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

