Effectiveness of Two New Endochin-like Quinolones, ELQ-596 and ELQ-650, in Experimental Mouse Models of Human Babesiosis
- PMID: 38563132
- PMCID: PMC11127568
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00143
Effectiveness of Two New Endochin-like Quinolones, ELQ-596 and ELQ-650, in Experimental Mouse Models of Human Babesiosis
Abstract
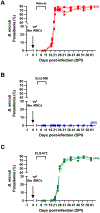
Endochin-like quinolones (ELQs) define a class of small molecule antimicrobials that target the mitochondrial electron transport chain of various human parasites by inhibiting their cytochrome bc1 complexes. The compounds have shown potent activity against a wide range of protozoan parasites, including the intraerythrocytic parasites Plasmodium and Babesia, the agents of human malaria and babesiosis, respectively. First-generation ELQ compounds were previously found to reduce infection by Babesia microti and Babesia duncani in animal models of human babesiosis but achieved a radical cure only in combination with atovaquone and required further optimization to address pharmacological limitations. Here, we report the identification of two second-generation 3-biaryl ELQ compounds, ELQ-596 and ELQ-650, with potent antibabesial activity in vitro and favorable pharmacological properties. In particular, ELQ-598, a prodrug of ELQ-596, demonstrated high efficacy as an orally administered monotherapy at 10 mg/kg. The compound achieved radical cure in both the chronic model of B. microti-induced babesiosis in immunocompromised mice and the lethal infection model induced by B. duncani in immunocompetent mice. Given its high potency, favorable physicochemical properties, and low toxicity profile, ELQ-596 represents a promising drug for the treatment of human babesiosis.
Keywords: B. duncani; B. microti; Babesia; ELQ-596; endochin-like quinolones; human babesiosis; parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
Choukri Ben Mamoun, Pratap Vydyam and Meenal Chand declare no conflict of interest. Sovitj Pou, Rolf W. Winter, Katherine M. Liebman, Aaron Nilsen, J. Stone Doggett, Michael K. Riscoe are listed as co-inventors of technology that is involved in this research and which has been licensed by OHSU for commercial development. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by OHSU and the Portland VAMC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radical cure of experimental babesiosis in immunodeficient mice using a combination of an endochin-like quinolone and atovaquone.J Exp Med. 2016 Jun 27;213(7):1307-18. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151519. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27270894 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Therapy Targeting Cytochrome bc1 Prevents Babesia Erythrocytic Development and Protects from Lethal Infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Aug 17;65(9):e0066221. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00662-21. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34152821 Free PMC article.
-
Endochin-like quinolone-300 and ELQ-316 inhibit Babesia bovis, B. bigemina, B. caballi and Theileria equi.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Dec 3;13(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04487-3. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 33272316 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Human Babesiosis: Then and Now.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 1;10(9):1120. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091120. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34578153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Babesiosis.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2022 Sep;36(3):655-670. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2022.02.009. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 36116841 Review.
Cited by
-
3-Position Biaryl Endochin-like Quinolones with Enhanced Antimalarial Performance.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 12;10(7):2419-2442. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00140. Epub 2024 Jun 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38862127 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro efficacy of next-generation dihydrotriazines and biguanides against babesiosis and malaria parasites.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Sep 4;68(9):e0042324. doi: 10.1128/aac.00423-24. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39136469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

