[Mutation spectrum analysis of 23-site chip neonatal deafness genetic screening]
- PMID: 38563166
- PMCID: PMC11387295
- DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.04.001
[Mutation spectrum analysis of 23-site chip neonatal deafness genetic screening]
Abstract
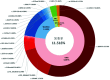
Objective:To analyze the mutation spectrum of 23-site chip newborn deafness genetic screening in Beijing, and to provide basis for genetic counseling and clinical diagnosis and treatment. Methods:The study included 21 006 babies born in Beijing from December 2022 to June 2023. All subjects underwent newborn deafness genetic screening in Beijing Tongren Hospital, covering 23 variants in 4 genes, the GJB2 gene(c.35delG, c.176_191del16, c.235delC, c.299_300delAT, c.109G>A, c.257C>G, c.512insAACG, c.427C>T, c.35insG), SLC26A4 gene(c.919-2A>G, c.2168A>G, c.1174A>T, c.1226G>A, c.1229C>T, c.1975G>C, c.2027T>A, c.589G>A, c.1707+5G>A, c.917insG, c.281C>T), Mt12SrRNA(m.1555A>G, m.1494C>T) and GJB3 gene(c.538C>T). The mutation detection rate and allele frequency were analyzed. Results:The overall mutation detection rate was 11.516%(2 419/21 006), with the GJB2 gene being the most frequently involved at 9.097%(1 911/21 006), followed by the SLC26A4 gene at 2.123%(446/21 006), the GJB3 gene at 0.362%(76/21 006) and Mt12SrRNA at 0.176%(37/21 006). Among the GJB2 genes, c.109G>A and c.235delC mutation detection rates were the highest, with 6.579%(1 382/21 006) and 1.795%(377/21 006), respectively. Of the SLC26A4 genes, c.919-2A>G and c.2168A>G had the highest mutation rates of 1.423%(299/21 006) and 0.233%(49/21 106), respectively. Regarding the allele frequency, GJB2 c.109G>A was the most common variant with an allele frequency of 3.359%(1 411/42 012), followed by the GJB2 c.235delC at 0.897%(377/42 012) and the SLC26A4 c.919-2A>G at 0.719%(302/42 012). Conclusion:23-site chip newborn deafness genetic screening in Beijing showed that GJB2 c.109G>A mutation detection rate and allele frequency were the highest. This study has enriched the epidemiological data of 23-site chip genetic screening mutation profiles for neonatal deafness, which can provide evidence for clinical practice.
目的:分析北京市23项新生儿耳聋基因筛查的突变频谱,为遗传咨询及临床诊疗提供依据。 方法:研究对象为2022年12月-2023年6月在首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院接受23项耳聋基因筛查的新生儿21 006例。23项耳聋基因筛查包括4个基因23个位点:GJB2基因(c.35delG、c.176_191del16、c.235delC、c.299_300delAT、c.109G>A、c.257C>G、c.512insAACG、c.427C>T、c.35insG)、SLC26A4基因(c.919-2A>G、c.2168A>G、c.1174A>T、c.1226G>A、c.1229C>T、c.1975G>C、c.2027T>A、c.589G>A、c.1707+5G>A、c.917insG、c.281C>T)、线粒体12SrRNA基因(m.1555A>G、m.1494C>T)和GJB3基因(c.538C>T)。分析各基因位点的突变率及等位基因突变频率。 结果:21 006例中,耳聋基因筛查未通过率11.516%(2 419/21 006)。4个基因中GJB2基因突变率最高,为9.097%(1 911/21 006),其次分别为SLC26A4基因2.123%(446/21 006)、GJB3基因0.362%(76/21 006)及线粒体12SrRNA基因0.176%(37/21 006)。GJB2基因中,c.109G>A和c.235delC突变率最高,分别为6.579%(1 382/21 006)和1.795%(377/21 006)。SLC26A4基因中,c.919-2A>G和c.2168A>G突变率最高,分别为1.423%(299/21 006)和0.233%(49/21 006)。等位基因突变频率,GJB2基因c.109G>A最高,为3.359%(1 411/42 012),其次为GJB2基因c.235delC,0.897%(377/42 012)及SLC26A4基因c.919-2A>G,0.719%(302/42 012)。 结论:北京市23项新生儿耳聋基因筛查提示,GJB2基因c.109G>A突变率和等位基因突变频率最高,值得临床重视。本研究丰富了23项新生儿耳聋基因筛查突变频谱的流行病学资料,可为临床提供依据。.
Keywords: allele frequency; deafness genes; mutation detection rate; newborn.
Copyright© by the Editorial Department of Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article and the planning committee members and staff have no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical