Recent advances in the development of 225Ac- and 211At-labeled radioligands for radiotheranostics
- PMID: 38564087
- PMCID: PMC11035452
- DOI: 10.1007/s44211-024-00514-w
Recent advances in the development of 225Ac- and 211At-labeled radioligands for radiotheranostics
Erratum in
-
Correction: Recent advances in the development of 225Ac- and 211At-labeled radioligands for radiotheranostics.Anal Sci. 2025 Jun;41(6):897. doi: 10.1007/s44211-025-00763-3. Anal Sci. 2025. PMID: 40199831 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
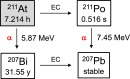
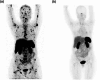
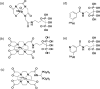
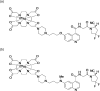
Radiotheranostics utilizes a set of radioligands incorporating diagnostic or therapeutic radionuclides to achieve both diagnosis and therapy. Imaging probes using diagnostic radionuclides have been used for systemic cancer imaging. Integration of therapeutic radionuclides into the imaging probes serves as potent agents for radionuclide therapy. Among them, targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is a promising next-generation cancer therapy. The α-particles emitted by the radioligands used in TAT result in a high linear energy transfer over a short range, inducing substantial damage to nearby cells surrounding the binding site. Therefore, the key to successful cancer treatment with minimal side effects by TAT depends on the selective delivery of radioligands to their targets. Recently, TAT agents targeting biomolecules highly expressed in various cancer cells, such as sodium/iodide symporter, norepinephrine transporter, somatostatin receptor, αvβ3 integrin, prostate-specific membrane antigen, fibroblast-activation protein, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 have been developed and have made remarkable progress toward clinical application. In this review, we focus on two radionuclides, 225Ac and 211At, which are expected to have a wide range of applications in TAT. We also introduce recent fundamental and clinical studies of radiopharmaceuticals labeled with these radionuclides.
Keywords: Cancer; Molecular Imaging; Radiopharmaceuticals; Radiotheranostics; Targeted alpha therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are pertinent to the content of this article.
Figures















Similar articles
-
Astatine-211 and actinium-225: two promising nuclides in targeted alpha therapy.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Nov 25;57(3):327-343. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024206. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39587859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Targeted Alpha-Particle Therapy. What We Learned about Recoils Release from In Vivo Generators.Molecules. 2018 Mar 5;23(3):581. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030581. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29510568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotheranostic landscape: A review of clinical and preclinical development.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jun;52(7):2685-2709. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07103-7. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39891713 Review.
-
A review of recent advancements in Actinium-225 labeled compounds and biomolecules for therapeutic purposes.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 Nov;102(5):1276-1292. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14311. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 37715360 Review.
-
Targeted Alpha Therapy: Current Clinical Applications.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Aug;35(6):404-417. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.3576. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 32552031 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the radionuclide theranostic concept through the radiohybrid approach.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Nov 25;16(5):1856-1864. doi: 10.1039/d4md00591k. eCollection 2025 May 22. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39618962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering a Radiohybrid PSMA Ligand with an Albumin-Binding Moiety and Pharmacokinetic Modulation via an Albumin-Binding Competitor for Radiotheranostics.Molecules. 2025 Jun 29;30(13):2804. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132804. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649319 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of an 211At-labeled RGD peptide and immune checkpoint blockade to enhance antitumor efficacy.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07498-3. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40768094 No abstract available.
-
Feasibility of targeted alpha therapy for Alzheimer's disease using 211At-labeled agent targeting amyloid-β aggregates.Ann Nucl Med. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s12149-025-02095-8. Online ahead of print. Ann Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40796687
-
Therapeutic potential of FAPI RLT in oncology: A systematic review.Theranostics. 2025 Mar 10;15(9):4084-4100. doi: 10.7150/thno.106108. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40213678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- K. Ogawa, Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 67, 897 (2019) - PubMed
-
- K. Mishiro, H. Hanaoka, A. Yamaguchi, K. Ogawa, Coord. Chem. Rev. 383, 104 (2019)
-
- F.D.C. Guerra Liberal, J.M. O’Sullivan, S.J. McMahon, K.M. Prise, Cancer Biother. Radiopharm.Biother. Radiopharm. 35, 404 (2020) - PubMed
-
- K. Ogawa, Anal. Sci. 40, 1 (2024) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

