NCS-1 protein regulates TRPA1 channel through the PI3K pathway in breast cancer and neuronal cells
- PMID: 38564162
- PMCID: PMC11074019
- DOI: 10.1007/s13105-024-01016-z
NCS-1 protein regulates TRPA1 channel through the PI3K pathway in breast cancer and neuronal cells
Abstract
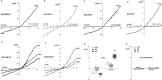
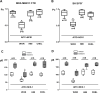
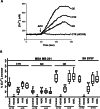
The physical and functional interaction between transient receptor potential channel ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) and neuronal calcium sensor 1 (NCS-1) was assessed. NCS-1 is a calcium (Ca2+) sensor found in many tissues, primarily neurons, and TRPA1 is a Ca2+ channel involved not only in thermal and pain sensation but also in conditions such as cancer and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, in which NCS-1 is also a regulatory component.We explored the interactions between these two proteins by employing western blot, qRT-PCR, co-immunoprecipitation, Ca2+ transient monitoring with Fura-2 spectrophotometry, and electrophysiology assays in breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) with different levels of NCS-1 expression and neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y).Our findings showed that the expression of TRPA1 was directly correlated with NCS-1 levels at both the protein and mRNA levels. Additionally, we found a physical and functional association between these two proteins. Physically, the NCS-1 and TRPA1 co-immunoprecipitate. Functionally, NCS-1 enhanced TRPA1-dependent Ca2+ influx, current density, open probability, and conductance, where the functional effects depended on PI3K. Conclusion: NCS-1 appears to act not only as a Ca2+ sensor but also modulates TRPA1 protein expression and channel function in a direct fashion through the PI3K pathway. These results contribute to understanding how Ca2+ homeostasis is regulated and provides a mechanism underlying conditions where Ca2+ dynamics are compromised, including breast cancer. With a cellular pathway identified, targeted treatments can be developed for breast cancer and neuropathy, among other related diseases.
Keywords: Calcium signaling; Cancer; Electrophysiology; NCS-1; Neuronal calcium sensor 1; Neurotoxicity; TRPA1; Transient receptor potential channel ankyrin 1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
BEE is a cofounder of Osmol Therapeutics, a company that is targeting NCS-1 for therapeutic purposes. The other authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NCS-1 expression is higher in basal breast cancers and regulates calcium influx and cytotoxic responses to doxorubicin.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jan;14(1):87-104. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12589. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31647602 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel Regulates TRPA1 Function and Expression Through PKA and PKC.Neurochem Res. 2023 Jan;48(1):295-304. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03748-0. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36098890 Free PMC article.
-
Discrete proteolysis of neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) by mu-calpain disrupts calcium binding.Cell Calcium. 2009 Oct;46(4):257-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.08.002. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Cell Calcium. 2009. PMID: 19732951 Free PMC article.
-
NCS-1 is a regulator of calcium signaling in health and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Nov;1865(11 Pt B):1660-1667. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29746899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular roles of neuronal calcium sensor-1 and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinases in fungi.J Basic Microbiol. 2011 Apr;51(2):120-8. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201000184. Epub 2010 Nov 12. J Basic Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21077122 Review.
References
-
- Apasu JE, Schuette D, LaRanger R, Steinle JA, Nguyen LD, Grosshans HK, Zhang M, Cai WL, Yan Q, Robert ME. Neuronal calcium sensor 1 (NCS1) promotes motility and metastatic spread of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):4802–4813. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802004R. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehmerle W, Splittgerber U, Lazarus MB, McKenzie KM, Johnston DG, Austin DJ, Ehrlich BE. Paclitaxel induces calcium oscillations via an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and neuronal calcium sensor 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(48):18356–18361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607240103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehmerle W, Splittgerber U, Lazarus MB, McKenzie KM, Johnston DG, Austin DJ, Ehrlich BE. Paclitaxel induces calcium oscillations via an inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor and neuronal calcium sensor 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(48):18356–18361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607240103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

