Quality of Large Language Model Responses to Radiation Oncology Patient Care Questions
- PMID: 38564215
- PMCID: PMC10988356
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.4630
Quality of Large Language Model Responses to Radiation Oncology Patient Care Questions
Abstract
Importance: Artificial intelligence (AI) large language models (LLMs) demonstrate potential in simulating human-like dialogue. Their efficacy in accurate patient-clinician communication within radiation oncology has yet to be explored.
Objective: To determine an LLM's quality of responses to radiation oncology patient care questions using both domain-specific expertise and domain-agnostic metrics.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study retrieved questions and answers from websites (accessed February 1 to March 20, 2023) affiliated with the National Cancer Institute and the Radiological Society of North America. These questions were used as queries for an AI LLM, ChatGPT version 3.5 (accessed February 20 to April 20, 2023), to prompt LLM-generated responses. Three radiation oncologists and 3 radiation physicists ranked the LLM-generated responses for relative factual correctness, relative completeness, and relative conciseness compared with online expert answers. Statistical analysis was performed from July to October 2023.
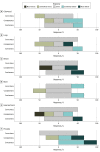
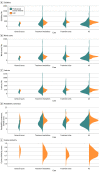
Main outcomes and measures: The LLM's responses were ranked by experts using domain-specific metrics such as relative correctness, conciseness, completeness, and potential harm compared with online expert answers on a 5-point Likert scale. Domain-agnostic metrics encompassing cosine similarity scores, readability scores, word count, lexicon, and syllable counts were computed as independent quality checks for LLM-generated responses.
Results: Of the 115 radiation oncology questions retrieved from 4 professional society websites, the LLM performed the same or better in 108 responses (94%) for relative correctness, 89 responses (77%) for completeness, and 105 responses (91%) for conciseness compared with expert answers. Only 2 LLM responses were ranked as having potential harm. The mean (SD) readability consensus score for expert answers was 10.63 (3.17) vs 13.64 (2.22) for LLM answers (P < .001), indicating 10th grade and college reading levels, respectively. The mean (SD) number of syllables was 327.35 (277.15) for expert vs 376.21 (107.89) for LLM answers (P = .07), the mean (SD) word count was 226.33 (191.92) for expert vs 246.26 (69.36) for LLM answers (P = .27), and the mean (SD) lexicon score was 200.15 (171.28) for expert vs 219.10 (61.59) for LLM answers (P = .24).
Conclusions and relevance: In this cross-sectional study, the LLM generated accurate, comprehensive, and concise responses with minimal risk of harm, using language similar to human experts but at a higher reading level. These findings suggest the LLM's potential, with some retraining, as a valuable resource for patient queries in radiation oncology and other medical fields.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of Ophthalmologist and Large Language Model Chatbot Responses to Online Patient Eye Care Questions.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Aug 1;6(8):e2330320. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30320. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37606922 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Answers of Generative Large Language Models Versus Peer Users for Interpreting Laboratory Test Results for Lay Patients: Evaluation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Apr 17;26:e56655. doi: 10.2196/56655. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 38630520 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating ChatGPT to test its robustness as an interactive information database of radiation oncology and to assess its responses to common queries from radiotherapy patients: A single institution investigation.Cancer Radiother. 2024 Jun;28(3):258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2023.11.005. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Cancer Radiother. 2024. PMID: 38866652
-
Exploring the role of artificial intelligence, large language models: Comparing patient-focused information and clinical decision support capabilities to the gynecologic oncology guidelines.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025 Feb;168(2):419-427. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.15869. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 39161265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-driven report-generation tools in mental healthcare: A review of commercial tools.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2025 May-Jun;94:150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2025.02.018. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40088857 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of Large Language Models on Medical Oncology Examination Questions.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jun 3;7(6):e2417641. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17641. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38888919 Free PMC article.
-
Bots in white coats: are large language models the future of patient education? A multicenter cross-sectional analysis.Int J Surg. 2025 Mar 1;111(3):2376-2384. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002250. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39878073 Free PMC article.
-
Application of large language models in disease diagnosis and treatment.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Jan 20;138(2):130-142. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003456. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39722188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Italian radiation oncologists use ChatGPT: a survey by the young group of the Italian association of radiotherapy and clinical oncology (yAIRO).Radiol Med. 2025 Apr;130(4):453-462. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01945-1. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Radiol Med. 2025. PMID: 39690359
-
Assessing the Quality and Reliability of ChatGPT's Responses to Radiotherapy-Related Patient Queries: Comparative Study With GPT-3.5 and GPT-4.JMIR Cancer. 2025 Apr 16;11:e63677. doi: 10.2196/63677. JMIR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40239208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoch CC, Wollenberg B, Lüers JC, et al. . ChatGPT’s quiz skills in different otolaryngology subspecialties: an analysis of 2576 single-choice and multiple-choice board certification preparation questions. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023;280(9):4271-4278. Published online June 7, 2023. doi:10.1007/s00405-023-08051-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doshi R, Amin K, Khosla P, Bajaj S, Chheang S, Forman HP. Utilizing large language models to simplify radiology reports: a comparative analysis of ChatGPT3.5, ChatGPT4.0, Google Bard, and Microsoft Bing. Published online June 7, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.06.04.23290786 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

