Lapatinib antitumor effect is associated with PI3K and MAPK pathway: An analysis in human and canine prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 38564578
- PMCID: PMC10986952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297043
Lapatinib antitumor effect is associated with PI3K and MAPK pathway: An analysis in human and canine prostate cancer cells
Abstract
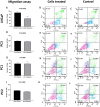
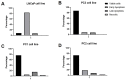
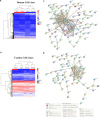
The aberrant activation of HER2 has a pivotal role in bone metastasis implantation and progression in several tumor types, including prostate cancer (PC). Trastuzumab and other anti-HER2 therapies, such as lapatinib, have been used in human breast cancer HER2 positive. Although HER2 overexpression has been reported in PC, anti-HER2 therapy response has revealed conflicting results. We investigated the potential of lapatinib in inhibiting cell migration and inducing apoptosis in two human (LNCaP and PC3) and two canine PC cell lines (PC1 and PC2). Cell migration and apoptosis were evaluated by Annexin V/PI analysis after lapatinib treatment. The transcriptome analysis of all cell lines before and after treatment with lapatinib was also performed. We found increased apoptosis and migration inhibition in LNCaP cells (androgen-sensitive cell line), while PC1, PC2, and PC3 cells showed no alterations after the treatment. The transcriptome analysis of LNCaP and PC3 cell lines showed 158 dysregulated transcripts in common, while PC1 and PC2 cell lines presented 82. At the doses of lapatinib used, we observed transcriptional modifications in all cell lines. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway were enriched in human PC cells, while canine PC cells showed enrichment of tyrosine kinase antitumor response and HER2-related pathways. In canine PC cells, the apoptosis failed after lapatinib treatment, possibly due to the downregulation of MAPK genes. Prostate cancer cells insensitive to androgens may be resistant to lapatinib through PI3K gene dysregulation. The association of lapatinib with PI3K inhibitors may provide a more effective antitumor response and clinical benefits to PC patients.
Copyright: © 2024 Fonseca-Alves et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lapatinib sensitivities of two novel trastuzumab-resistant HER2 gene-amplified gastric cancer cell lines.Gastric Cancer. 2014;17(3):450-62. doi: 10.1007/s10120-013-0290-6. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Gastric Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23948998
-
Roles of BIM induction and survivin downregulation in lapatinib-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells with HER2 amplification.Oncogene. 2011 Sep 29;30(39):4097-106. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.111. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21499301
-
PTK6 inhibition promotes apoptosis of Lapatinib-resistant Her2(+) breast cancer cells by inducing Bim.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 19;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0594-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26084280 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases.Clin Ther. 2008 Aug;30(8):1426-47. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.08.008. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18803986 Review.
-
Overcoming treatment resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer: potential strategies.Drugs. 2012 Jun 18;72(9):1175-93. doi: 10.2165/11634000-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22686613 Review.
Cited by
-
Amiloride sensitizes prostate cancer cells to the reversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib by modulating Erbb3 subcellular localization.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Dec 27;82(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05540-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39725713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schatzl G, Madersbacher S, Thurridl T, Waldmuller J, Kramer G, Haitel A, et al.. High-Grade ProstateCancer IsAssociatedWith LowSerumTestosterone Levels. Testosterone and Prostate Cancer 2001;47:52–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

