Quality adjustment and analysis of human resource prices in China: Based on a hedonic price model
- PMID: 38564590
- PMCID: PMC10986967
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297352
Quality adjustment and analysis of human resource prices in China: Based on a hedonic price model
Abstract
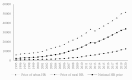
The competition in the world has shifted from natural resources and capital resources to human resources. The human resources have become the real power source of the economic growth. Firstly, the price of human resources in China is calculated. Secondly, in order to measure the human resources quality adjustment index, the indicators system is constructed. Third, the Hedonic method is used to calculate the human resources "pure price" of 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government) in China. The "pure price" has no the factor of human resources quality. Lastly, comparing the price of human resources before and after quality adjustment. The results show that: first, the number of human resources in China increased continuously during 1995-2015 and decreased during 2016-2020. Second, the price of nominal human resources in China keeps rising. In 2020, the nominal price is 39,087 yuan per person which is 15.44 times as many as in 1995. Thirdly, after the quality adjustment, the price of human resources has decreased significantly. The multiple between the actual and nominal price of human resources is between 1.75 and 2.12. Fourthly, the province with high human resource quality adjustment index generally have high quality human resource level or quantity. Fifth, the top five provinces of actual human resource prices are Shanghai, Beijing, Guangdong, Tianjin, Zhejiang, the bottom five provinces are Guizhou, Yunnan, Henan, Xizang, Gansu. Finally, the paper puts forward some policy recommendations: Improving the data collection mechanism of human resources accounting to provide a basic guarantee for the accurate accounting of human resources. Improving the price of human resources in the central and western regions to attract the talents to transfer to the central and western regions. Enhancing the skills training of human resources to improve the quality of human resources in the western region.
Copyright: © 2024 Lan Ma. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Spatial Correlations of Health Resource Agglomeration Capacities and Their Influencing Factors: Evidence from China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 23;17(22):8705. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228705. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33238597 Free PMC article.
-
The economy-employment-environmental health transfer and embedded inequities of China's capital metropolitan area: a mixed-methods study.Lancet Planet Health. 2023 Nov;7(11):e912-e924. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(23)00218-8. Lancet Planet Health. 2023. PMID: 37940211
-
The gap of economic development expanding between eastern China and middle, western China.China Popul Res Newsl. 1996 Jun;(1):2-3. China Popul Res Newsl. 1996. PMID: 12347362
-
[Malaria situation in the People's Republic of China in 2011].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Dec 30;30(6):419-22. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23484249 Chinese.
-
[Malaria situation in the People's Republic of China in 2002].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2003;21(4):193-6. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14628361 Chinese.
References
-
- Marx Engels. The Complete Works of Marx and Engels. People’s Press, Beijing, China. 1963:412.
-
- Smith A. A Study of the Nature and Causes of National Wealth. The Commercial Press, Beijing, China. 1979:47–58.
-
- Li H, Tang T. Regional differences in labor quality based on human capital. Journal of Central University of Finance and Economics. 2015(08):72–80+86.
-
- Huang S, Zhu L, Sheng X. Research on the impact of human resource quality on employee income in listed companies based on propensity score matching method. Journal of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology. 2016,37(02):42–45.
-
- Yue C, Qiu W, Zhu Y. The present situation and prospects of the development of high quality human resources in China. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition). 2020(01):120–132.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

