The IRG1-itaconate axis protects from cholesterol-induced inflammation and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38564634
- PMCID: PMC11009655
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2400675121
The IRG1-itaconate axis protects from cholesterol-induced inflammation and atherosclerosis
Abstract
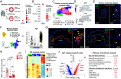
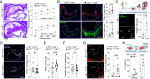
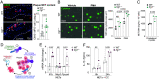
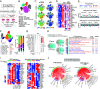
Atherosclerosis is fueled by a failure to resolve lipid-driven inflammation within the vasculature that drives plaque formation. Therapeutic approaches to reverse atherosclerotic inflammation are needed to address the rising global burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Recently, metabolites have gained attention for their immunomodulatory properties, including itaconate, which is generated from the tricarboxylic acid-intermediate cis-aconitate by the enzyme Immune Responsive Gene 1 (IRG1/ACOD1). Here, we tested the therapeutic potential of the IRG1-itaconate axis for human atherosclerosis. Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), we found that IRG1 is up-regulated in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions compared to patient-matched healthy vasculature, and in mouse models of atherosclerosis, where it is primarily expressed by plaque monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. Global or hematopoietic Irg1-deficiency in mice increases atherosclerosis burden, plaque macrophage and lipid content, and expression of the proatherosclerotic cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β. Mechanistically, absence of Irg1 increased macrophage lipid accumulation, and accelerated inflammation via increased neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation and NET-priming of the NLRP3-inflammasome in macrophages, resulting in increased IL-1β release. Conversely, supplementation of the Irg1-itaconate axis using 4-octyl itaconate (4-OI) beneficially remodeled advanced plaques and reduced lesional IL-1β levels in mice. To investigate the effects of 4-OI in humans, we leveraged an ex vivo systems-immunology approach for CVD drug discovery. Using CyTOF and scRNA-seq of peripheral blood mononuclear cells treated with plasma from CVD patients, we showed that 4-OI attenuates proinflammatory phospho-signaling and mediates anti-inflammatory rewiring of macrophage populations. Our data highlight the relevance of pursuing IRG1-itaconate axis supplementation as a therapeutic approach for atherosclerosis in humans.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; immunometabolism; innate immunity; macrophage; neutrophil.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:K.J.M. is on the scientific advisory Board of Beren Therapeutics and Bitterroot Bio. K.J.M. and A.M.S. have patents and patent applications through NYU Grossman School of Medicine that have been submitted/published and that are not related to the work detailed in this manuscript. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Soehnlein O., Multiple roles for neutrophils in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 110, 875–888 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL131481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL167568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM136542/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI139374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL098129/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL146367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135799/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153712/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139909/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143639/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL165258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL144993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

