Glia Development and Function in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 38565269
- PMCID: PMC11445397
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041346
Glia Development and Function in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is a powerful experimental setting for uncovering fundamental tenets of nervous system organization and function. Its nearly invariant and simple anatomy, coupled with a plethora of methodologies for interrogating single-gene functions at single-cell resolution in vivo, have led to exciting discoveries in glial cell biology and mechanisms of glia-neuron interactions. Findings over the last two decades reinforce the idea that insights from C. elegans can inform our understanding of glial operating principles in other species. Here, we summarize the current state-of-the-art, and describe mechanistic insights that have emerged from a concerted effort to understand C. elegans glia. The remarkable acceleration in the pace of discovery in recent years paints a portrait of striking molecular complexity, exquisite specificity, and functional heterogeneity among glia. Glial cells affect nearly every aspect of nervous system development and function, from generating neurons, to promoting neurite formation, to animal behavior, and to whole-animal traits, including longevity. We discuss emerging questions where C. elegans is poised to fill critical knowledge gaps in our understanding of glia biology.
Copyright © 2024 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
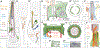
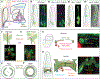
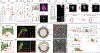

Similar articles
-
Molecular profiling of invertebrate glia.Glia. 2025 Mar;73(3):632-656. doi: 10.1002/glia.24623. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Glia. 2025. PMID: 39415317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial development and function in the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jan 8;7(4):a020578. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020578. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25573712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glia-Neuron Interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jul 8;42:149-168. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050314. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30883261 Review.
-
Glia-neuron interactions in the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006 Oct;16(5):522-8. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2006.08.001. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16935487 Review.
-
Glia actively sculpt sensory neurons by controlled phagocytosis to tune animal behavior.Elife. 2021 Mar 24;10:e63532. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63532. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33759761 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuron cilia restrain glial KCC-3 to a microdomain to regulate multisensory processing.Cell Rep. 2024 Mar 26;43(3):113844. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113844. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38421867 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron cilia constrain glial regulators to microdomains around distal neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 18:2023.03.18.533255. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.18.533255. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36993507 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Molecular profiling of invertebrate glia.Glia. 2025 Mar;73(3):632-656. doi: 10.1002/glia.24623. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Glia. 2025. PMID: 39415317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial Regulation of Circuit Wiring, Firing, and Expiring in the Drosophila Central Nervous System.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024 Dec 2;16(12):a041347. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041347. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024. PMID: 38565270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2024 Oct 7;228(2):iyae116. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae116. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 39167071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aida T, Yoshida J, Nomura M, Tanimura A, Iino Y, Soma M, Bai N, Ito Y, Cui W, Aizawa H, et al. 2015. Astroglial glutamate transporter deficiency increases synaptic excitability and leads to pathological repetitive behaviors in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 40: 1569–1579. doi:10.1038/npp.2015.26 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
