Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
- PMID: 38565633
- PMCID: PMC10987664
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58462-4
Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
Abstract
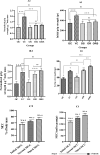
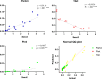
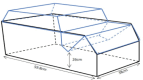
This study aimed to determine the effects of resistance training combined with a probiotic supplement enriched with vitamin D and leucine on sestrin2, oxidative stress, antioxidant defense, and mitophagy markers in aged Wistar rats. Thirty-five male rats were randomly assigned to two age groups (old with 18-24 months of age and young with 8-12 weeks of age) and then divided into five groups, including (1) old control (OC: n = 5 + 2 for reserve in all groups), (2) young control (YC: n = 5), (3) old resistance training (OR: n = 5), (4) old resistance training plus supplement (ORS: n = 5), and old supplement group (OS: n = 5). Training groups performed ladder climbing resistance training 3 times per week for 8 weeks. Training intensity was inserted progressively, with values equal to 65, 75, and 85, determining rats' maximal carrying load capacity. Each animal made 5 to 8 climbs in each training session, and the time of each climb was between 12 and 15 s, although the time was not the subject of the evaluation, and the climbing pattern was different in the animals. Old resistance plus supplement and old supplement groups received 1 ml of supplement 5 times per week by oral gavage in addition to standard feeding, 1 to 2 h post training sessions. Forty-eight hours after the end of the training program, 3 ml of blood samples were taken, and all rats were then sacrificed to achieve muscle samples. After 8 weeks of training, total antioxidant capacity and superoxide dismutase activity levels increased in both interventions. A synergistic effect of supplement with resistance training was observed for total antioxidant capacity, superoxide dismutase, and PTEN-induced kinase 1. Sestrin 2 decreased in intervention groups. These results suggest that resistance training plus supplement can boost antioxidant defense and mitophagy while potentially decreasing muscle strength loss.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sobhon P, Savedvanich G, Weerakiet S. Oxidative stress and inflammation: The root causes of aging. Explor. Med. 2023;4:127–156.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

