Tumor associated microglia/macrophages utilize GPNMB to promote tumor growth and alter immune cell infiltration in glioma
- PMID: 38566120
- PMCID: PMC10985997
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-024-01754-7
Tumor associated microglia/macrophages utilize GPNMB to promote tumor growth and alter immune cell infiltration in glioma
Abstract
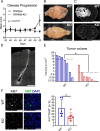
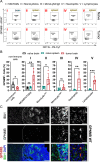
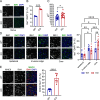
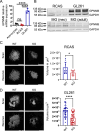
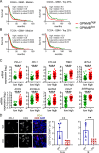
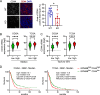
Tumor-associated microglia and blood-derived macrophages (TAMs) play a central role in modulating the immune suppressive microenvironment in glioma. Here, we show that GPNMB is predominantly expressed by TAMs in human glioblastoma multiforme and the murine RCAS-PDGFb high grade glioma model. Loss of GPNMB in the in vivo tumor microenvironment results in significantly smaller tumor volumes and generates a pro-inflammatory innate and adaptive immune cell microenvironment. The impact of host-derived GPNMB on tumor growth was confirmed in two distinct murine glioma cell lines in organotypic brain slices from GPNMB-KO and control mice. Using published data bases of human glioma, the elevated levels in TAMs could be confirmed and the GPNMB expression correlated with a poorer survival.
Keywords: CD44; Experimental glioma; GPNMB; Glioblastoma; Macrophage; Microglia; Mouse; RCAS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

