Unusual Locations of Inverted Papilloma
- PMID: 38566729
- PMCID: PMC10982235
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04398-6
Unusual Locations of Inverted Papilloma
Abstract
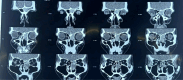
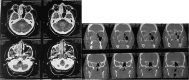
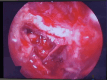
Inverted papilloma is a tumor found involving the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. They are not cancerous but can be locally aggressive. They are most commonly seen involving the lateral wall of nose and maxillary sinus. When the tumor involves the frontal sinus and sphenoid sinus or the post ethmoid cells it presents a surgical challenge. Inverted papilloma almost always occur unilateraly and affect mainly the maxillary sinus. Inverted papilloma arising from the sphenoid and frontal sinuses are rare. Here we present two cases; one involving a 60 year man, with inverted papilloma originating from the frontal sinus and another case where it originated from the sphenoid sinus anterior wall and posterior ethmoidalcell (Onodi cell) and was resected endoscopically.
Keywords: Frontal sinus; Inverted papilloma; Sphenoid sinus.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic surgical treatment of nasal and paranasal sinus inverted papilloma.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993 Dec;109(6):988-95. doi: 10.1177/019459989310900603. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993. PMID: 8265198 Review.
-
[Inverted papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses--diagnosis, surgical procedure and studies of cytokeratin profile].Laryngorhinootologie. 1997 Apr;76(4):216-24. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-997415. Laryngorhinootologie. 1997. PMID: 9264595 German.
-
Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: clinical data, surgical strategy and recurrence rates.Acta Otolaryngol. 2000 Mar;120(2):267-72. doi: 10.1080/000164800750001071. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000. PMID: 11603788
-
Sphenoid sinus inverted papilloma: a case report and literature review.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Jul;18(3):332-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1370761. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 25992117 Free PMC article.
-
Inverted papilloma with bilateral origin. A case report and review of the literature.Ann Ital Chir. 2022 Oct 5;11:S2239253X22038294. Ann Ital Chir. 2022. PMID: 36259423 Review.
References
-
- Shutter NB, Citardi MJ, Batra PS. Minimally invasive resection of frontal recess/sinus inverted papilloma. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2007;28:221–224. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
