Identification of Specific Cell Surface Markers on Immune Cells of Squirrel Monkeys (Saimiri sciureus)
- PMID: 38566886
- PMCID: PMC10985276
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/8215195
Identification of Specific Cell Surface Markers on Immune Cells of Squirrel Monkeys (Saimiri sciureus)
Abstract
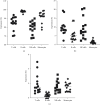
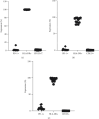
Nonhuman primates are an important experimental model for the development of targeted biological therapeutics because of their immunological closeness to humans. However, there are very few antibody reagents relevant for delineating the different immune cell subsets based on nonhuman primate antigens directly or with cross-reactivity to those in humans. Here, we report specific expression of HLA-DR, PD-1, and CD123 on different circulating immune cell subsets in the peripheral blood that included T cells (CD3+), T cells subsets (CD4+ and CD8+), B cells (CD20+), natural killer (NK) cells (CD3-CD16+), and natural killer T cells (CD3+CD16+) along with different monocyte subsets in squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). We established cross-reactivity of commercial mouse antihuman monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), with these various immune cell surface markers. These findings should aid further future comprehensive understanding of the immune parameters and identification of new biomarkers to significantly improve SQM as a model for biomedical studies.
Copyright © 2024 Bharti P. Nehete et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abee C. R. The squirrel monkey in biomedical research. ILAR Journal . 1989;31(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/ilar.31.1.11. - DOI
-
- Maestripieri D., Roney J. R. Evolutionary developmental psychology: contributions from comparative research with nonhuman primates. Developmental Review . 2006;26(2):120–137. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2006.02.006. - DOI
-
- Corr J. Social behavior in aged rhesus macaques. Collegium Antropologicum . 2003;27(1):87–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

