The multi-faceted nature of age-associated osteoporosis
- PMID: 38566930
- PMCID: PMC10985042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2024.101750
The multi-faceted nature of age-associated osteoporosis
Abstract
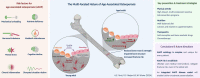
Age-associated osteoporosis (AAOP) poses a significant health burden, characterized by increased fracture risk due to declining bone mass and strength. Effective prevention and early treatment strategies are crucial to mitigate the disease burden and the associated healthcare costs. Current therapeutic approaches effectively target the individual contributing factors to AAOP. Nonetheless, the management of AAOP is complicated by the multitude of variables that affect its development. Main intrinsic and extrinsic factors contributing to AAOP risk are reviewed here, including mechanical unloading, nutrient deficiency, hormonal disbalance, disrupted metabolism, cognitive decline, inflammation and circadian disruption. Furthermore, it is discussed how these can be targeted for prevention and treatment. Although valuable as individual targets for intervention, the interconnectedness of these risk factors result in a unique etiology for every patient. Acknowledgement of the multifaceted nature of AAOP will enable the development of more effective and sustainable management strategies, based on a holistic, patient-centered approach.
Keywords: Age-associated osteoporosis; Fracture risk; Osteoporosis etiology; Personalized care; Prevention strategies.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Adams S., Sello C.T., Qin G.-X., Che D., Han R. Does dietary Fiber affect the levels of nutritional components after feed formulation? Fibers. 2018;6(2):29. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6439/6/2/29
-
- Almeida M., Han L., Martin-Millan M., Plotkin L.I., Stewart S.A., Roberson P.K., Kousteni S., O’Brien C.A., Bellido T., Parfitt A.M., Weinstein R.S., Jilka R.L., Manolagas S.C. Skeletal involution by age-associated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282(37):27285–27297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702810200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

