Immune and behavioral correlates of protection against symptomatic post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 38566991
- PMCID: PMC10985347
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1287504
Immune and behavioral correlates of protection against symptomatic post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
Introduction: We sought to determine pre-infection correlates of protection against SARS-CoV-2 post-vaccine inzfections (PVI) acquired during the first Omicron wave in the United States.
Methods: Serum and saliva samples from 176 vaccinated adults were collected from October to December of 2021, immediately before the Omicron wave, and assessed for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-specific IgG and IgA binding antibodies (bAb). Sera were also assessed for bAb using commercial assays, and for neutralization activity against several SARS-CoV-2 variants. PVI duration and severity, as well as risk and precautionary behaviors, were assessed by questionnaires.
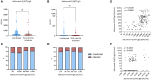
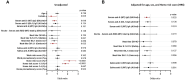
Results: Serum anti-Spike IgG levels assessed by research assay, neutralization titers against Omicron subvariants, and low home risk scores correlated with protection against PVIs after multivariable regression analysis. Commercial assays did not perform as well as research assay, likely due to their lower dynamic range.
Discussion: In the 32 participants that developed PVI, anti-Spike IgG bAbs correlated with lower disease severity and shorter duration of illness.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; correlates of immunity; respiratory infection; vaccination.
Copyright © 2024 Goguet, Olsen, Meyer, Ansari, Powers, Conner, Coggins, Wang, Wang, Illinik, Sanchez Edwards, Jackson-Thompson, Hollis-Perry, Wang, Alcorta, Wong, Saunders, Mohammed, Balogun, Kobi, Kosh, Bishop-Lilly, Cer, Arnold, Voegtly, Fitzpatrick, Luquette, Malagon, Ortega, Parmelee, Davies, Lindrose, Haines-Hull, Moser, Samuels, Rekedal, Graydon, Malloy, Tribble, Burgess, Campbell, Robinson, Broder, O’Connell, Weiss, Pollett, Laing and Mitre.
Conflict of interest statement
SP, TB, and DT report that the USU IDCRP, a U.S. Department of Defense DoD Institution, and the HJF were funded under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement to conduct an unrelated phase III COVID-19 monoclonal antibody immunoprophylaxis trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. The HJF, in support of the USU IDCRP, was funded by the DoD Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear Defense to augment the conduct of an unrelated phase III vaccine trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. Both trials were part of the USG COVID-19 response. Neither is related to the work presented here. Authors WM and SA were employed by the company Quest Diagnostics. Author JP was employed by company Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc. Authors LV, MF, AL and FM were employed by company Leidos. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




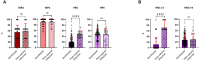
References
-
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard, 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2023). Available at: https://covid19.who.int/.
-
- Vivaldi G, Jolliffe DA, Faustini S, Shields AM, Holt H, Perdek N, et al. . Correlation between postvaccination anti-spike antibody titers and protection against breakthrough severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: A population-based longitudinal study. J Infect Dis. (2022) 226:1903–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac321 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

