Psychiatry and Family Medicine Residents' Likelihood of Prescribing HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis to Patients With Mental Illness and HIV Vulnerability
- PMID: 38567904
- PMCID: PMC11687185
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003423
Psychiatry and Family Medicine Residents' Likelihood of Prescribing HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis to Patients With Mental Illness and HIV Vulnerability
Abstract
Background: People living with mental illness (PLMI) experience disproportionately high incidence of and vulnerability to HIV. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is an effective and safe HIV prevention method, but data regarding prescription to PLMI are lacking. Psychiatrists may serve as important points of access for PrEP prescription for PLMI.
Methods: We conducted a vignette-based study of residents in psychiatry and family medicine (FM) to assess likelihood of prescribing PrEP and assumptions about the fictional patient. Participants were randomized to one of five vignettes in which the patients' psychiatric diagnosis was varied (schizophrenia on long-acting injectable or oral antipsychotic, bipolar disorder, major depression) or a control vignette without a psychiatric diagnosis.
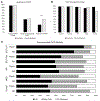
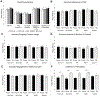
Results: A total of 439 residents participated. We found that high percentages of psychiatry (96.8%) and FM (97.4%) residents were aware of PrEP. High percentages of psychiatry (92.0%-98.1%) and FM (80.8%-100%) residents reported that PrEP was indicated for all patient conditions. Family medicine residents were more likely to prescribe PrEP to all experimental conditions than psychiatry residents. There was no difference in likelihood of prescribing to the control condition without a psychiatric diagnosis. The belief that PrEP prescription was out of scope of practice was greater among psychiatry residents.
Conclusions: A majority of psychiatry residents responded that PrEP was indicated for an array of patients with psychiatric diagnoses. However, psychiatry residents were broadly less likely to prescribe PrEP to patients with these diagnoses. The high percentage of psychiatry residents who reported that PrEP was indicated for all patients suggests that additional training is needed to facilitate PrEP prescription by psychiatrists.
Copyright © 2024 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

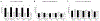
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Preexposure Prophylaxis for the Prevention of HIV Infection in the United States - 2021 Update – A Clinical Practice Guideline. 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
-
- Bauer-Staeb C, Jörgensen L, Lewis G, Dalman C, Osborn DPJ, Hayes JF. Prevalence and risk factors for HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C in people with severe mental illness: a total population study of Sweden. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4(9):685–693. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(17)30253-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

