Taqman PACMAN: a simple molecular approach for positive rapid antigen test confirmation during periods of low prevalence
- PMID: 38567975
- PMCID: PMC11064490
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.04073-23
Taqman PACMAN: a simple molecular approach for positive rapid antigen test confirmation during periods of low prevalence
Abstract
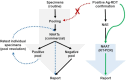
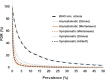
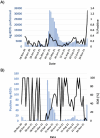
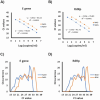
Antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) were widely deployed to enhance SARS-CoV-2 testing capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Consistent with national guidance for low prevalence settings, positive Ag-RDTs were confirmed using nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) to avoid false positive results. However, increasing demands for positive Ag-RDT confirmation competed with other testing priorities in clinical laboratories. This work hypothesized that real-time RT-PCR without nucleic acid extraction (NAE) would be sufficiently sensitive to support positive Ag-RDT confirmation. Ag-RDT and NAAT results from community-based asymptomatic testing sites prior to the omicron variant wave were compared to calculate the weekly false positive rate (FPR) and false detection rate (FDR). Real-time RT-PCR was compared with and without NAE using 752 specimens previously tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 using commercial NAATs and 344 specimens from Ag-RDT-positive individuals. The impact of SARS-CoV-2 prevalence on laboratory resources required to sustain Ag-RDT confirmation was modeled for the RT-PCR with and without NAE. Overall, FPR was low [0.07% (222/330,763)] in asymptomatic testing sites, but FDR was high [30.7% (222/724)]. When RT-PCR was compared with and without NAE, 100% concordance was obtained with NAAT-positive specimens, including those from Ag-RDT-positive individuals. NAE-free RT-PCR significantly reduced time to results, human resources, and overall costs. A 30.7% FDR reaffirms the need for NAAT-based confirmation of positive Ag-RDT results during low SARS-CoV-2 prevalence. NAE-free RT-PCR was shown to be a simple and cost-sparing NAAT-based solution for positive Ag-RDT confirmation, and its implementation supported data-driven broader Ag-RDT deployment into communities, workplaces, and households.
Importance: Rapid antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2 was widely deployed during the COVID-19 pandemic. In settings of low prevalence, national guidance recommends that positive antigen test results be confirmed with molecular testing. Given the high testing burden on clinical laboratories during the COVID-19 pandemic, the high volume of positive antigen tests submitted for confirmatory testing posed challenges for laboratory workflow. This study demonstrated that a simple PCR method without prior nucleic acid purification is an accurate and cost-effective solution for positive rapid antigen test confirmation. Implementing this method allowed molecular confirmatory testing for positive antigen tests to be sustained as antigen testing was expanded into large populations such as workplaces, schools, and households.
Keywords: COVID-19; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; extraction; false positive; molecular; prevalence; rapid antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of RT-PCR and antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) for SARS-CoV-2 detection: performance, variant specificity, and clinical implications.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0007324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00073-24. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38683014 Free PMC article.
-
Avoiding False-Positive SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test Results with Point-of-Care Molecular Testing on Residual Test Buffer.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0063922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00639-22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35863036 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Nasal and Nasopharyngeal Swabs for SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Detection in an Asymptomatic Population, and Direct Confirmation by RT-PCR from the Residual Buffer.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0245521. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02455-21. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35171010 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 24;3(3):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. PMID: 33760236 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Rapid antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2-a synopsis of the medical evidence.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023 Oct;107(2):116027. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2023.116027. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37516068 Review.
References
-
- Safiabadi Tali SH, LeBlanc JJ, Sadiq Z, Oyewunmi OD, Camargo C, Nikpour B, Armanfard N, Sagan SM, Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. 2021. Tools and techniques for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 detection. Clin Microbiol Rev 34:e00228-20. doi:10.1128/CMR.00228-20 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

