RhoA/rho kinase pathway activation in age-associated endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombosis
- PMID: 38568071
- PMCID: PMC10989549
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18153
RhoA/rho kinase pathway activation in age-associated endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombosis
Abstract
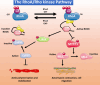
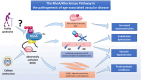
The small GTPase RhoA and the downstream Rho kinase (ROCK) regulate several cell functions and pathological processes in the vascular system that contribute to the age-dependent risk of cardiovascular disease, including endothelial dysfunction, excessive permeability, inflammation, impaired angiogenesis, abnormal vasoconstriction, decreased nitric oxide production and apoptosis. Frailty is a loss of physiological reserve and adaptive capacity with advanced age and is accompanied by a pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidative state that promotes vascular dysfunction and thrombosis. This review summarises the role of the RhoA/Rho kinase signalling pathway in endothelial dysfunction, the acquisition of the pro-thrombotic state and vascular ageing. We also discuss the possible role of RhoA/Rho kinase signalling as a promising therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of age-related cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: RhoA/rho kinase pathway; ageing; cardiovascular disease; endothelial dysfunction; frailty; thrombosis.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division . World Population Ageing 2017 – Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/397). 2017.
-
- Garcia‐Garcia FJ, Gutierrez Avila G, Alfaro‐Acha A, et al. The prevalence of frailty syndrome in an older population from Spain. The Toledo study for healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2011;15(10):852‐856. - PubMed
-
- Hoogendijk EO, Afilalo J, Ensrud KE, Kowal P, Onder G, Fried LP. Frailty: implications for clinical practice and public health. Lancet. 2019;394(10206):1365‐1375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

