Transcription factor regulation of ribosomal RNA in hematopoiesis
- PMID: 38568093
- PMCID: PMC11139577
- DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000816
Transcription factor regulation of ribosomal RNA in hematopoiesis
Abstract
Purpose of review: Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are transcribed within nucleoli from rDNA repeats by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I). There is variation in rRNA transcription rates across the hematopoietic tree, and leukemic blast cells have prominent nucleoli, indicating abundant ribosome biogenesis. The mechanisms underlying these variations are poorly understood. The purpose of this review is to summarize findings of rDNA binding and Pol I regulation by hematopoietic transcription factors.
Recent findings: Our group recently used custom genome assemblies optimized for human and mouse rDNA mapping to map nearly 2200 ChIP-Seq datasets for nearly 250 factors to rDNA, allowing us to identify conserved occupancy patterns for multiple transcription factors. We confirmed known rDNA occupancy of MYC and RUNX factors, and identified new binding sites for CEBP factors, IRF factors, and SPI1 at canonical motif sequences. We also showed that CEBPA degradation rapidly leads to reduced Pol I occupancy and nascent rRNA in mouse myeloid cells.
Summary: We propose that a number of hematopoietic transcription factors bind rDNA and potentially regulate rRNA transcription. Our model has implications for normal and malignant hematopoiesis. This review summarizes the literature, and outlines experimental considerations to bear in mind while dissecting transcription factor roles on rDNA.
Copyright © 2024 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High-resolution Sequencing Reveals that the Paf1 Complex May be a Conserved Transcription Elongation Factor for Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase I.J Mol Biol. 2025 Sep 1;437(17):169220. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169220. Epub 2025 May 19. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40398673
-
Control of ribosomal RNA synthesis by hematopoietic transcription factors.Mol Cell. 2022 Oct 20;82(20):3826-3839.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.08.027. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 36113481 Free PMC article.
-
Specific DNA features of the RNA polymerase I core promoter element targeted by core factor.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025 Jun;1868(2):195088. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2025.195088. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025. PMID: 40216226
-
Interpreting the Origins and Functions of Noncoding RNAs From the Ribosomal Genes.J Cell Physiol. 2025 Aug;240(8):e70080. doi: 10.1002/jcp.70080. J Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40765316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ribosomal RNA transcription landscapes of Plasmodium falciparum and related apicomplexan parasites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf641. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf641. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40626563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of Ribosomal RNA Transcription and Abundance in Normal and Leukemic Hematopoiesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 1:2025.08.01.668217. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.01.668217. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766528 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The role of lipoprotein‑associated phospholipase A2 in inflammatory response and macrophage infiltration in sepsis and the regulatory mechanisms.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Sep 30;24(5):178. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01460-6. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39343830
-
Active RNA synthesis patterns nuclear condensates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 13:2024.10.12.614958. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.12.614958. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39498261 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Hori Y, Engel C, Kobayashi T. Regulation of ribosomal RNA gene copy number, transcription and nucleolus organization in eukaryotes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023; 24:414–429. - PubMed
-
- Antony C, George SS, Blum J, et al. Control of ribosomal RNA synthesis by hematopoietic transcription factors. Mol Cell 2022; 82:3826–3839; e9. - PMC - PubMed
-
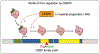
Profile of hematopoietic transcription factor-rDNA binding, and demonstration that CEBPA degradation leads to rapid reduction in rRNA transcription.
-
- Mills EW, Green R. Ribosomopathies: there’s strength in numbers. Science 2017; 358:eaan2755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

