Metabolic score for insulin resistance predicts major adverse cardiovascular event in premature coronary artery disease
- PMID: 38568104
- PMCID: PMC11042949
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205710
Metabolic score for insulin resistance predicts major adverse cardiovascular event in premature coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) index serves as a simple surrogate marker for insulin resistance (IR) and is associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD). However, the prognostic significance of METS-IR in patients with premature CAD remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the prognostic value of METS-IR in premature CAD.
Methods: This retrospective study included 582 patients diagnosed with premature CAD between December 2012 and July 2019. The median follow-up duration was 63 months (interquartile range, 44-81 months). The primary endpoint was Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE), defined as a composite of all-cause death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), repeat coronary artery revascularization, and non-fatal stroke.
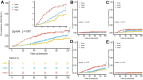
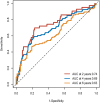
Results: Patients with MACE had significantly higher METS-IR levels than those without MACE (44.88±8.11 vs. 41.68±6.87, p<0.001). Kaplan-Meier survival curves based on METS-IR tertiles demonstrated a statistically significant difference (log-rank test, p<0.001). In the fully adjusted model, the Hazard Ratio (95% CI) for MACE was 1.41 (1.16-1.72) per SD increase in METS-IR, and the P for trend based on METS-IR tertiles was 0.001 for MACE. Time-dependent Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) analysis of METS-IR yielded an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.74 at 2 years, 0.69 at 4 years, and 0.63 at 6 years.
Conclusions: METS-IR serves as a reliable prognostic predictor of MACE in patients with premature CAD. Therefore, METS-IR may be considered a novel, cost-effective, and dependable indicator for risk stratification and early intervention in premature CAD.
Keywords: insulin resistance; major adverse cardiovascular events; metabolic score for insulin resistance; premature coronary artery disease; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Triglyceride-glucose index in the prediction of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with premature coronary artery disease: a retrospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jul 29;21(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01576-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35906587 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic score for insulin resistance in the prediction of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients after coronary artery bypass surgery: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 Jul 17;15(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01133-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37461067 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index as a suitable non-insulin-based insulin resistance marker to predict cardiovascular events in patients undergoing complex coronary artery intervention: a large-scale cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jan 6;23(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02110-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38184591 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of risk, severity, and prognosis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jul 6;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01906-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37415168 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Resistance and Coronary Artery Disease: Untangling the Web of Endocrine-Cardiac Connections.Cureus. 2023 Dec 25;15(12):e51066. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51066. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38269234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of triglyceride-glucose index and estimated glucose disposal rate with outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Cumulative effect and mediation analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 23;20(7):e0328150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328150. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40700433 Free PMC article.
-
Association between metabolic score for insulin resistance and stroke: a nationally representative cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007-2018.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1478884. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1478884. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39830199 Free PMC article.
-
The non-linear relationship between the metabolic score for insulin resistance and three-month outcomes in the individuals with acute ischemic stroke: a prospective Korean cohort study.BMC Neurol. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04299-x. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40618038 Free PMC article.
-
Association of METS-IR index with Type 2 Diabetes: A cross-sectional analysis of national health and nutrition examination survey data from 2009 to 2018.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 8;19(11):e0308597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308597. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39514584 Free PMC article.
-
Does diabetes status modify the association between the triglyceride-glucose index and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 4;24(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02890-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40760488 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

