The Feulgen reaction at the electron microscopy level
- PMID: 38568205
- PMCID: PMC11017718
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2024.3989
The Feulgen reaction at the electron microscopy level
Abstract
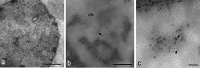
The Feulgen reaction has been the first specific method for detecting DNA available at light microscopy since 1924. However, a similar specific method was proposed for electron microscopy only 50 years later. Here, we discuss the problems encountered in finding the electrondense reagent capable of taking advantage of the extremely high resolution offered by electron microscopy as well as some applications of the method.
Figures

References
-
- Hayat H. Stains and cytochemical methods. New York: Plenum Press; 1993. pp. 254-60.
-
- Feulgen R, Rossenbeck H. [Mikroskopisch-chemischer Nachweis einer Nukleinsäure von Typus der Thymonukleinsäure und die darauf beruhende selektive Färbung von Zellkernen in mikroskopischen Präparaten]. [Article in German]. Hoppe-Seylers Z Physiol Chem 1924;135:203-48.
-
- Gautier A. Ultrastructural localization of DNA in ultrathin tissue sections. Int Rev Cytol 1976;44:113-91. - PubMed
-
- Moyne G. Methods in ultrastructural cytochemistry of the cell nucleus. Prog Histochem Cytochem 1980;13:1-72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

