Cardiometabolic characteristics of people with metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity
- PMID: 38569471
- PMCID: PMC11025492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.03.002
Cardiometabolic characteristics of people with metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity
Abstract
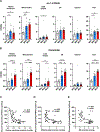
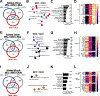
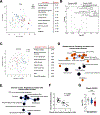
There is considerable heterogeneity in the cardiometabolic abnormalities associated with obesity. We evaluated multi-organ system metabolic function in 20 adults with metabolically healthy obesity (MHO; normal fasting glucose and triglycerides, oral glucose tolerance, intrahepatic triglyceride content, and whole-body insulin sensitivity), 20 adults with metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO; prediabetes, hepatic steatosis, and whole-body insulin resistance), and 15 adults who were metabolically healthy lean. Compared with MUO, people with MHO had (1) altered skeletal muscle biology (decreased ceramide content and increased expression of genes involved in BCAA catabolism and mitochondrial structure/function); (2) altered adipose tissue biology (decreased expression of genes involved in inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling and increased expression of genes involved in lipogenesis); (3) lower 24-h plasma glucose, insulin, non-esterified fatty acids, and triglycerides; (4) higher plasma adiponectin and lower plasma PAI-1 concentrations; and (5) decreased oxidative stress. These findings provide a framework of potential mechanisms responsible for MHO and the metabolic heterogeneity of obesity. This study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02706262).
Keywords: adipose tissue; beta cell function; insulin resistance; insulin sensitivity; metabolically healthy obesity; obesity; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.K. serves on scientific advisory boards for Altimmune, Merck, Scholar Rock, and CinFina Pharma. R.A.B. receives royalty income related to the CompBio method developed by R.A.B. and licensed by Washington University to PercayAI. M.Y. is currently an employee of Eli Lilly Japan.
Figures

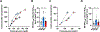
References
-
- Mongraw-Chaffin M, Foster MC, Anderson CAM, Burke GL, Haq N, Kalyani RR, Ouyang P, Sibley CT, Tracy R, Woodward M, et al. (2018). Metabolically Healthy Obesity, Transition to Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 71, 1857–1865. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

