Spatial transcriptomics reveals discrete tumour microenvironments and autocrine loops within ovarian cancer subclones
- PMID: 38570491
- PMCID: PMC10991508
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47271-y
Spatial transcriptomics reveals discrete tumour microenvironments and autocrine loops within ovarian cancer subclones
Abstract
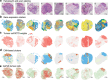
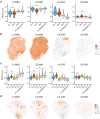
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) is genetically unstable and characterised by the presence of subclones with distinct genotypes. Intratumoural heterogeneity is linked to recurrence, chemotherapy resistance, and poor prognosis. Here, we use spatial transcriptomics to identify HGSOC subclones and study their association with infiltrating cell populations. Visium spatial transcriptomics reveals multiple tumour subclones with different copy number alterations present within individual tumour sections. These subclones differentially express various ligands and receptors and are predicted to differentially associate with different stromal and immune cell populations. In one sample, CosMx single molecule imaging reveals subclones differentially associating with immune cell populations, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. Cell-to-cell communication analysis identifies subclone-specific signalling to stromal and immune cells and multiple subclone-specific autocrine loops. Our study highlights the high degree of subclonal heterogeneity in HGSOC and suggests that subclone-specific ligand and receptor expression patterns likely modulate how HGSOC cells interact with their local microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Paul A. Cohen reports speakers’ honoraria from AstraZeneca and Seqirus, and consultancy fees and stock in Clinic IQ Pty Ltd. Emily Killingbeck is an employee of NanoString Technologies and holds NanoString stock or stock options. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

