Inhibitory effect of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.) extract on body weight gain in rats on a high-fat diet
- PMID: 38571539
- PMCID: PMC10985764
- DOI: 10.5114/pg.2023.130142
Inhibitory effect of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.) extract on body weight gain in rats on a high-fat diet
Abstract
Introduction: The leaves and seeds of Urtica dioica (UD) are used in folk treatments for many diseases. Anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiallergenic properties of UD have been reported.
Aim: To uncover the effects of nettle seed (Urtica dioica; UD) extract on body weight gain in rats on a high-fat diet (HFD).
Material and methods: Male Wistar albino rats (n = 32) were divided into 4 groups, comprising a control group, a group that received a HFD (HFD group), a group that received UD extracts (UD group), and a group that received a HFD as well as UD extracts (HFD + UD group). UD extracts were given a daily dose of 300 mg/kg of body weight orally for 75 days.
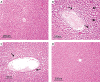
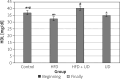
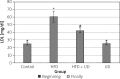
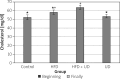
Results: The HFD led to weight gain that was partially moderated by the UD extract. Histopathological findings in the HFD + UD group were uniformly significantly lower than those in the HFD group. Serum alanine transaminase, alanine aminotransferase, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein levels were significantly higher in the HFD group than in the HFD + UD group, and the HDL levels were lower in the HFD group than in the control group and the HFD + UD group.
Conclusions: The cholesterol levels were discovered to be highest in the HFD + UD group. Therefore, it was concluded that the UD extract did not completely protect the rats against body weight gain.
Keywords: Urtica dioica; body weight gain; histopathology.
Copyright © 2024 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective effect of Urtica dioica leaf hydro alcoholic extract against experimentally-induced atherosclerosis in rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2018 May-Jun;8(3):254-262. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2018. PMID: 29881711 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and Urtica Dioica extract ameliorate mitochondrial function and the expression of cardiac muscle Nuclear Respiratory Factor 2 and Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-alpha in STZ-induced diabetic rats.Gene. 2022 May 15;822:146351. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146351. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35189251
-
Urtica dioica attenuates ovalbumin-induced inflammation and lipid peroxidation of lung tissues in rat asthma model.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1561-1568. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1310905. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 28385108 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of pharmacological uses of Urtica dioica and others benefits.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;150:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31163183 Review.
-
Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica L.): Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Compounds, and Food Functional Properties.Molecules. 2022 Aug 16;27(16):5219. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165219. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altunkaynak BZ, Özbek E. Obesity: causes and treatment alternatives. Van Med J 2006; 13: 138-142.
-
- Alarcon-Aguilar FJ, Zamilpa A, Perez-Garcia MD, et al. . Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa on obesity in MSG mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2007; 114: 66-71. - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH, York DA, Rössner S, et al. . Prevention Conference VII: obesity, a worldwide epidemic related to heart disease and stroke: executive summary. Circulation 2004; 110: 2968-75. - PubMed
-
- Hasani-Ranjbar S, Larijani B, Abdollahi M. A systematic review of the potential herbal sources of future drugs effective in oxidant-related diseases. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 2009; 8: 2-10. - PubMed
-
- Abdollahi M, Afshar-Imani B. A review on obesity and weight loss measures. Middle East Pharmacy 2003; 11: 6-10.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
