Expression of HIF‑α and their association with clinicopathological parameters in clinical renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38571885
- PMCID: PMC10989218
- DOI: 10.48101/ujms.v129.9407
Expression of HIF‑α and their association with clinicopathological parameters in clinical renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the cellular localization and expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) -α proteins (specifically HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α) that play a role in the hypoxia pathway and to determine their correlation with clinicopathological parameters and patient survival in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Materials and methods: Tissue microarray (TMA) with cores from 150 clear cell RCCs and 31 non-ccRCC samples. HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α antibodies were used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) of TMA to evaluate the cellular localization and expression levels of HIF-α proteins, specifically in relation to the hypoxia pathway.
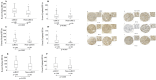
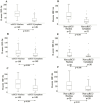
Results: The expression levels of the HIF-α proteins were higher in the nucleus than in the cytoplasm. Furthermore, the nuclear expression levels of all HIF-α proteins were significantly higher in clear cell RCC (ccRCC) than in non-ccRCC. Cytoplasmic HIF-3α expression was also higher in ccRCC than in non-ccRCC, whereas cytoplasmic HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression levels were similar between the different RCC types. In ccRCC, nuclear HIF-1α expression levels correlated with both nuclear HIF-2α and HIF-3α levels, whereas cytoplasmic HIF-3α expression levels were associated with HIF-1α only.In non-ccRCC, there was a positive correlation observed between nuclear HIF-1α and HIF-3α expression, but no correlation was found with HIF-2α. In patients with ccRCC, the nuclear expressions of HIF-1α and HIF-3α was significantly associated with cancer-specific survival (CSS) in univariate analysis. This association was no longer evident in multivariate analysis. Notably, there was no correlation observed between nuclear HIF-2α expression and CSS in these patients. In contrast, cytoplasmic expression levels showed no association with CSS.
Conclusion: The expression levels of the three primary HIF-α proteins were found to be higher in the nucleus than in the cytoplasm. Furthermore, the results indicated that HIF-3α and HIF-1α expression levels were significant univariate factors associated with CSS in patients with clear cell RCC. These results highlight the critical role that HIF-3α and HIF-1α play in the hypoxia pathway.
Keywords: HIF-1α; HIF-2α; HIF-3α; and tumor stage; ccRCC; non-ccRCC; prognosis; renal cell carcinoma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Upsala Medical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Poor prognosis and advanced clinicopathological features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) are associated with cytoplasmic subcellular localisation of Hypoxia inducible factor-2α.Eur J Cancer. 2014 May;50(8):1531-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24565854
-
[The expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1,2 alpha in sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinoma and their relationships to the mutations of von Hippel-Lindau gene].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Mar 15;43(6):390-3. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15854350 Chinese.
-
[Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha, hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in sporadic clear cell renal cell renal cell carcinoma and their significance in the pathogenesis thereof].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Jun 13;86(22):1526-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16854277 Chinese.
-
Multiplicity of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors and their connection to the circadian clock in the zebrafish.Physiol Biochem Zool. 2015 Mar-Apr;88(2):146-57. doi: 10.1086/679751. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Physiol Biochem Zool. 2015. PMID: 25730270 Review.
-
Targeting HIF-2 α in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A promising therapeutic strategy.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Mar;111:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28259286 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Erythropoietin Activity in Clear Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3777. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083777. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332447 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
