Eubacterium coprostanoligenes alleviates chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis by enhancing intestinal mucus barrier
- PMID: 38572095
- PMCID: PMC10985029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.12.015
Eubacterium coprostanoligenes alleviates chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis by enhancing intestinal mucus barrier
Abstract
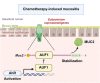
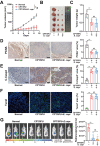
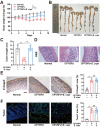
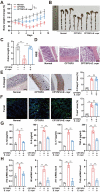
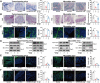
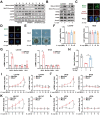
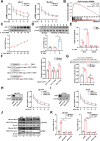
Chemotherapy-induced mucositis represents a severe adverse outcome of cancer treatment, significantly curtailing the efficacy of these treatments and, in some cases, resulting in fatal consequences. Despite identifying intestinal epithelial cell damage as a key factor in chemotherapy-induced mucositis, the paucity of effective treatments for such damage is evident. In our study, we discovered that Eubacterium coprostanoligenes promotes mucin secretion by goblet cells, thereby fortifying the integrity of the intestinal mucus barrier. This enhanced barrier function serves to resist microbial invasion and subsequently reduces the inflammatory response. Importantly, this effect remains unobtrusive to the anti-tumor efficacy of chemotherapy drugs. Mechanistically, E. copr up-regulates the expression of AUF1, leading to the stabilization of Muc2 mRNA and an increase in mucin synthesis in goblet cells. An especially significant finding is that E. copr activates the AhR pathway, thereby promoting the expression of AUF1. In summary, our results strongly indicate that E. copr enhances the intestinal mucus barrier, effectively alleviating chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis by activating the AhR/AUF1 pathway, consequently enhancing Muc2 mRNA stability.
Keywords: AUF1; Chemotherapy; Eubacterium coprostanoligenes; MUC2; Mucositis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Docimo R., Anastasio M.D., Bensi C. Chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022;23:501–511. - PubMed
-
- De Pietri S., Weischendorff S., Rathe M., Frandsen T.L., Hasle H., Nersting J., et al. Gastrointestinal barrier integrity and mucosal inflammation as risk factors of blood stream infections in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Int J Cancer. 2023;153:1635–1642. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

