CGRWDL: alignment-free phylogeny reconstruction method for viruses based on chaos game representation weighted by dynamical language model
- PMID: 38572227
- PMCID: PMC10987876
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1339156
CGRWDL: alignment-free phylogeny reconstruction method for viruses based on chaos game representation weighted by dynamical language model
Abstract
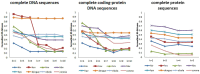
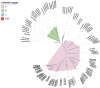
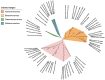
Traditional alignment-based methods meet serious challenges in genome sequence comparison and phylogeny reconstruction due to their high computational complexity. Here, we propose a new alignment-free method to analyze the phylogenetic relationships (classification) among species. In our method, the dynamical language (DL) model and the chaos game representation (CGR) method are used to characterize the frequency information and the context information of k-mers in a sequence, respectively. Then for each DNA sequence or protein sequence in a dataset, our method converts the sequence into a feature vector that represents the sequence information based on CGR weighted by the DL model to infer phylogenetic relationships. We name our method CGRWDL. Its performance was tested on both DNA and protein sequences of 8 datasets of viruses to construct the phylogenetic trees. We compared the Robinson-Foulds (RF) distance between the phylogenetic tree constructed by CGRWDL and the reference tree by other advanced methods for each dataset. The results show that the phylogenetic trees constructed by CGRWDL can accurately classify the viruses, and the RF scores between the trees and the reference trees are smaller than that with other methods.
Keywords: alignment-free method; chaos game representation; dynamical language model; k-mers; virus phylogeny reconstruction.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Yu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Whole genome/proteome based phylogeny reconstruction for prokaryotes using higher order Markov model and chaos game representation.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016 Mar;96:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.12.011. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016. PMID: 26724405
-
Fast and accurate genome comparison using genome images: The Extended Natural Vector Method.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2019 Dec;141:106633. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106633. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2019. PMID: 31563612
-
A phylogenetic analysis of the brassicales clade based on an alignment-free sequence comparison method.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Aug 29;3:192. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00192. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22952468 Free PMC article.
-
Chaos game representation and its applications in bioinformatics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Nov 10;19:6263-6271. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.11.008. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34900136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numerical Characterization of DNA Sequences for Alignment-free Sequence Comparison - A Review.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(3):365-380. doi: 10.2174/1386207324666210811101437. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 34382516 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting viral host codon fitness and path shifting through tree-based learning on codon usage biases and genomic characteristics.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 10;15(1):12251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91469-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40211017 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

