Study on the effect and mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus AFY06 on inflammation-associated colorectal cancer induced by AOM/DSS in mice
- PMID: 38572238
- PMCID: PMC10987852
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1382781
Study on the effect and mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus AFY06 on inflammation-associated colorectal cancer induced by AOM/DSS in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus AFY06 (LR-AFY06) is a microorganism isolated from naturally fermented yogurt in Xinjiang, China.
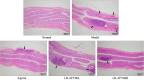
Methods: In this study, we investigated the effects and mechanisms of LR-AFY06 in a mouse model of inflammation-associated colon cancer. The mouse model was established by azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS) induction. The tumor number in intestinal tissues was counted, and the histopathological analysis was performed on colon tissues. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to measure relevant protein levels in colon tissues.
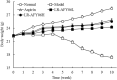
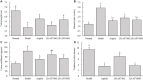
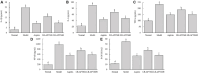
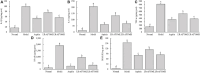
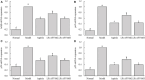
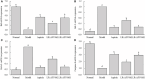
Results: LR-AFY06 treatment alleviated weight loss, increased organ index, reduced intestinal tumor incidence, improved histopathological damage, decreased the levels of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in the serum and colon tissue, downregulated the mRNA expression of inhibitor of NF-κB beta (IκBβ), p65, p50, p52, B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), and B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) in colon tissues, and increased the mRNA expression of Bid and caspase-8. The high concentration of LR-AFY06 exerted a better effect than the low concentration; however, the effect was slightly inferior to that of aspirin. Moreover, LR-AFY06 mitigated the intestinal inflammatory process and inhibited intestinal tumor development by regulating the NF-κB and apoptosis pathways.
Discussion: The present study indicates the regulatory potential of LR-AFY06 in inflammation-associated colorectal cancer in mice, providing a valuable basis for further research.
Keywords: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus; azoxymethane; colon cancer; mRNA; mice.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Zhang, Li, Yu, Lai and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemopreventive Effect of Aster glehni on Inflammation-Induced Colorectal Carcinogenesis in Mice.Nutrients. 2018 Feb 12;10(2):202. doi: 10.3390/nu10020202. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29439531 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 17β-estradiol on colorectal cancer development after azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium treatment of ovariectomized mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;164:139-151. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30981879
-
Jianpi Qingchang decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 21;23(7):1180-1188. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1180. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28275298 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC04 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice is associated with modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Nov;102(11):9570-9585. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16840. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 31477303
-
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LS8 Ameliorates Azoxymethane/Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis in Mice via Regulating Gut Microbiota and Inhibiting Inflammation.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022 Oct;14(5):947-959. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09967-9. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022. PMID: 35788907
Cited by
-
Targeting cholesterol-driven pyroptosis: a promising strategy for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 15;52(1):459. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10554-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40372511 Review.
-
The processed Sanguisorba officinalis L. triterpenoids prevent colon cancer through the TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway, combined with network pharmacology, molecular simulation dynamics and experimental verification.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1605326. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605326. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agah S., Alizadeh A. M., Mosavi M., Ranji P., Khavari-Daneshvar H., Ghasemian F., et al. (2019). More protection of Lactobacillus acidophilus than Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics on azoxymethane-induced mouse colon cancer. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 11 857–864. 10.1007/s12602-018-9425-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

