A systematic review of binge drinking interventions and bias assessment among college students and young adults in high-income countries
- PMID: 38572263
- PMCID: PMC10988166
- DOI: 10.1017/gmh.2024.24
A systematic review of binge drinking interventions and bias assessment among college students and young adults in high-income countries
Abstract
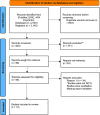
Alcohol is the number one substance used by young people and people of college age. Binge drinking (BD) in this age group is considered one of the most important global health issues, as much harm accrues from it and even lives are lost. This study aimed to review the interventions to curb BD or encourage responsible drinking among college students and young adults. MEDLINE (PubMed), ERIC and APA PsycINFO were searched. The selected articles were published in English and had to evaluate a BD reduction program through a randomized control trial (RCT) among college students or young adults between the ages of 17-24 years. The exclusion criteria included research not published in English, systematic review articles, qualitative studies, designs other than RCTs and discussion articles on college students drinking with no findings. The three reviewers independently screened and extracted the data using the PRISMA guidelines. The overall quality of the studies was assessed. Then, 10 of the 12 interventions studied were found to be successful in reducing BD among college students, though the effect sizes were small to medium. A minority of the studies used behavior change theories. Effective interventions for reducing BD among college students and young adults should include robust behavior change theories, longer follow-up time and the operationalization of multiple outcomes. Process evaluation is needed to be conducted in these studies.
Keywords: binge drinking; college students; heavy episodic drinking; interventions; problem drinking; young adults.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Protocol for a systematic review of the factors associated with binge drinking among adolescents and young adults.Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 11;6(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0461-3. Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28399900 Free PMC article.
-
Mobility management to prevent, reduce, or delay driving a car in teenagers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 16;8(8):CD009438. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009438.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32799320 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of combined alcohol and sexual risk taking reduction interventions on the sexual behaviour of teenagers and young adults: a systematic review.Public Health. 2019 Aug;173:83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31255962
Cited by
-
Global scientific research landscape on binge drinking: a comprehensive bibliometric and visualization analysis of trends, collaborations, and future directions.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2025 Mar 10;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13011-025-00641-1. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2025. PMID: 40065367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Addiction Centers (2023) Substance Abuse Statistics among young adults. Retrieved from https://americanaddictioncenters.org/addiction-statistics/young-adults.
-
- Bridges LS and Sharma M (2015) A systematic review of interventions aimed at reducing binge drinking among college students. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 59, 25–47. https://www.jstor.org/stable/48506447. - PubMed
-
- Courtney KE and Polich J (2009) Binge drinking in young adults: Data, definitions, and determinants. Psychological Bulletin 135, 142–156. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2748736/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Das JK, Salam RA, Arshad A, Finkelstein Y and Bhutta ZA (2016) Interventions for adolescent substance abuse: An overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Adolescent Health 59, S61–S75. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5026681/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources