Antibody-drug conjugates targeting HER2 for the treatment of urothelial carcinoma: potential therapies for HER2-positive urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 38572425
- PMCID: PMC10987710
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1326296
Antibody-drug conjugates targeting HER2 for the treatment of urothelial carcinoma: potential therapies for HER2-positive urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
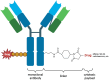
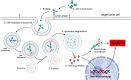
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is a common cancer characterized by high morbidity and mortality rates. Despite advancements in treatment, challenges such as recurrence and low response rates persist. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have emerged as a promising therapeutic approach for various cancers, although their application in UC is currently limited. This review focuses on recent research regarding ADCs designed to treat UC by targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), a surface antigen expressed on tumor cells. ADCs comprise three main components: an antibody, a linker, and a cytotoxic payload. The antibody selectively binds to tumor cell surface antigens, facilitating targeted delivery of the cytotoxic drug, while linkers play a crucial role in ensuring stability and controlled release of the payload. Cleavable linkers release the drug within tumor cells, while non-cleavable linkers ensure stability during circulation. The cytotoxic payload exerts its antitumor effect by disrupting cellular pathways. HER2 is commonly overexpressed in UCs, making it a potential therapeutic target. Several ADCs targeting HER2 have been approved for cancer treatment, but their use in UC is still being tested. Numerous HER2 ADCs have demonstrated significant growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in translational models of HER2-overexpressing bladder cancer. Ongoing clinical trials are assessing the efficacy and safety of ADCs targeting HER2 in UC, with the aim of determining tumor response and the potential of ADCs as a treatment option for UC patients. The development of effective therapies with improved response rates and long-term effectiveness is crucial for advanced and metastatic UC. ADCs targeting HER2 show promise in this regard and merit further investigation for UC treatment.
Keywords: ErbB2; bladder neoplasm; human epidermal growth factor receptor; metastasis; systemic therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Shih, Lin, Luo and Sung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review of recent advancements in antibody-drug and bicycle toxin conjugates for the treatment of urothelial cancer.Ther Adv Urol. 2024 May 20;16:17562872241249073. doi: 10.1177/17562872241249073. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2024. PMID: 38779496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of antibody-drug conjugates in treating breast cancer with different HER2 status.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Jan 3;17:17588359241311379. doi: 10.1177/17588359241311379. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39759831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapy-Induced Senescence Enhances the Efficacy of HER2-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 16;82(24):4670-4679. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0787. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36222720 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Solid Tumor Oncology: An Effectiveness Payday with a Targeted Payload.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 19;15(8):2160. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082160. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementing antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) in HER2-positive breast cancer: state of the art and future directions.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 11;23(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01459-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34380530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular biomarkers of progression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer - beyond conventional risk stratification.Nat Rev Urol. 2025 Feb;22(2):75-91. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00914-7. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Nat Rev Urol. 2025. PMID: 39095581 Review.
-
New Advances in Metastatic Urothelial Cancer: A Narrative Review on Recent Developments and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 7;25(17):9696. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179696. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Urothelial Cancer: From Scientific Rationale to Clinical Development.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;16(13):2420. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132420. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-drug conjugate combinations in cancer treatment: clinical efficacy and clinical study perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 21;16:1556245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1556245. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40061961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A radiomics-based interpretable machine learning model to predict the HER2 status in bladder cancer: a multicenter study.Insights Imaging. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01840-3. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39466475 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

